투석
투석은 신장 기능이 저하된 개인을 위한 치료법입니다. 투석에는 혈액투석과 복막투석이라는 두 가지 유형이 있으며 둘 다 정상적인 신장 기능을 수행하고 혈액에서 노폐물과 과잉 체액을 걸러냅니다.
절차 세부사항
위험/이점
회복과 전망
의사에게 전화해야 할 때
내용물
개요
절차 세부사항
위험/이점
회복과 전망
의사에게 전화해야 할 때
개요
투석 중인 환자의 사진
투석이란 무엇입니까?
투석은 신장 기능이 저하된 사람들을 위한 치료법입니다. 신부전증이 있으면 신장이 혈액을 제대로 여과하지 못합니다. 결과적으로 노폐물과 독소가 혈류에 쌓이게 됩니다. 투석은 신장의 기능을 수행하여 혈액에서 노폐물과 과도한 체액을 제거합니다.
투석이 필요한 사람은 누구입니까?
신부전 또는 말기 신장 질환(ESRD)이 있는 사람은 투석이 필요할 수 있습니다. 고혈압, 당뇨병, 루푸스와 같은 부상이나 상태는 신장을 손상시켜 신장 질환을 유발할 수 있습니다.
어떤 사람들에게는 알려진 이유 없이 신장 문제가 발생합니다. 신부전은 장기간 지속될 수도 있고, 심각한 질병이나 부상을 입은 후 갑자기(급성) 발생할 수도 있습니다. 이러한 유형의 신부전은 회복되면서 사라질 수 있습니다.
신장질환에는 5단계가 있습니다. 5단계 신장 질환의 경우 의료 서비스 제공자는 귀하를 말기 신장 질환(ESRD) 또는 신부전 상태로 간주합니다. 이 시점에서 신장은 정상 기능의 약 10~15%를 수행하고 있습니다. 생명을 유지하려면 투석이나 신장 이식이 필요할 수도 있습니다. 어떤 사람들은 이식을 기다리는 동안 투석을 받습니다.
신장은 어떤 일을 하나요?
신장은 비뇨기계의 일부입니다. 이 두 개의 콩 모양 기관은 척추 양쪽의 흉곽 아래에 위치합니다. 그들은 혈액에서 독소를 제거하여 여과되고 영양이 풍부한 혈액을 혈류로 되돌립니다.
노폐물과 여분의 수분이 소변을 만들어 신장에서 방광으로 이동합니다. 신장은 또한 혈압을 조절하는 데 도움이 됩니다.
절차 세부사항
투석에는 어떤 종류가 있나요?
투석을 받는 방법에는 두 가지가 있습니다.
혈액 투석.
복막 투석.
혈액투석이란 무엇입니까?
혈액투석의 경우, 기계가 신체에서 혈액을 제거하고 투석기(인공 신장)를 통해 이를 여과한 후 깨끗해진 혈액을 신체로 반환합니다. 이 3~5시간 과정은 일주일에 3번 병원이나 투석 센터에서 진행될 수 있습니다.
집에서도 혈액투석을 할 수 있습니다. 각 세션당 더 적은 시간 동안 일주일에 4~7회 재택 치료가 필요할 수 있습니다. 밤에 자는 동안 집에서 혈액투석을 하도록 선택할 수도 있습니다.
혈액투석 전에는 어떻게 되나요?
혈액투석을 시작하기 전에 혈류에 더 쉽게 접근할 수 있도록 간단한 수술 절차를 거칩니다. 다음이 있을 수 있습니다.
동정맥루(AV 누공): 외과의사가 팔의 동맥과 정맥을 연결합니다.
동정맥 이식편(AV 이식편): 동맥과 정맥이 연결하기에 너무 짧은 경우, 의사는 이식편(부드러운 속이 빈 튜브)을 사용하여 동맥과 정맥을 연결합니다.
AV 누공 및 이식편은 연결된 동맥과 정맥을 확대하여 투석 접근을 더 쉽게 만듭니다. 또한 혈액이 몸 안팎으로 더 빨리 흐르도록 도와줍니다.
투석이 신속하게 이루어져야 하는 경우, 담당 의사는 임시 접근을 위해 목, 가슴 또는 다리의 정맥에 카테터(얇은 튜브)를 삽입할 수 있습니다.
담당 의료 제공자는 누공이나 이식편의 감염을 예방하는 방법을 가르쳐줄 것입니다. 이 서비스 제공자는 귀하가 원할 경우 집에서 혈액투석을 실시하는 방법도 알려드릴 것입니다.
혈액투석 중에는 어떤 일이 발생하나요?
혈액투석 중 투석기는 다음을 수행합니다.
팔에 있는 바늘에서 혈액을 제거합니다.
투석기 필터를 통해 혈액을 순환시켜 노폐물을 투석액으로 옮깁니다. 이 클렌징 액에는 물, 소금 및 기타 첨가물이 포함되어 있습니다.
팔에 있는 다른 바늘을 통해 여과된 혈액을 몸으로 되돌려 보냅니다.
혈압을 모니터링하여 혈액이 몸 안팎으로 흐르는 속도를 조정합니다.
혈액투석 후에는 어떻게 되나요?
어떤 사람들은 혈액투석 중이나 직후에 저혈압을 경험합니다. 메스꺼움, 현기증 또는 현기증을 느낄 수 있습니다.
혈액투석의 다른 부작용은 다음과 같습니다.
가슴 통증이나 허리 통증.
두통.
가려운 피부.
근육 경련.
하지불안증후군.
복막투석이란 무엇입니까?
복막 투석을 하면 복부 내막(복막) 내부의 작은 혈관이 투석액의 도움을 받아 혈액을 걸러냅니다. 이 용액은 물, 소금, 기타 첨가물이 함유된 일종의 클렌징 리퀴드입니다.
복막투석은 집에서 시행됩니다. 이 치료를 수행하는 방법에는 두 가지가 있습니다.
자동 복막투석은 사이클러(cycler)라는 기계를 사용합니다.
지속적 외래 복막투석(CAPD)은 수동으로 시행됩니다.
복막투석 전에는 어떤 일이 발생하나요?
복막투석을 시작하기 약 3주 전에 간단한 수술을 받게 됩니다. 외과 의사는 부드럽고 얇은 튜브(카테터)를 배를 통해 복막에 삽입합니다. 이 카테터는 영구적으로 제자리에 유지됩니다.
의료 서비스 제공자가 방법을 가르쳐 줄 것입니다.
집에서 복막투석을 실시하고 카테터 부위의 감염을 예방합니다.
복막투석 중에는 어떤 일이 발생하나요?
복막 투석 중에는 다음이 수행됩니다.
카테터를 Y자형 튜브의 한 가지에 연결합니다. 이 튜브는 투석액이 담긴 백에 연결됩니다. 용액은 튜브와 카테터를 통해 복막강으로 흐릅니다.
약 10분 후 백이 비워지면 튜브와 카테터를 분리합니다.
카테터의 뚜껑을 닫습니다.
복막강 내부의 투석액이 신체의 노폐물과 여분의 체액을 흡수하는 동안 일상적인 활동을 계속하십시오. 이 프로세스는 60~90분 정도 걸릴 수 있습니다.
카테터에서 캡을 제거하고 Y자형 튜브의 다른 쪽 가지를 사용하여 수액을 깨끗하고 빈 백에 배출합니다.
이 단계를 하루에 최대 4번까지 반복하세요. 밤새도록 뱃속에 용액을 넣은 채 잠을 잔다.
어떤 사람들은 밤에 복막투석을 하는 것을 선호합니다. 자동 복막 투석을 사용하면, 사이클러라는 기계가 잠자는 동안 체액을 몸 안팎으로 펌핑합니다.
복막투석 후에는 어떻게 되나요?
뱃속의 액체로 인해 배가 부풀어 오르거나 포만감을 느낄 수 있습니다. 불편함을 느낄 수도 있지만 치료는 고통스럽지 않습니다. 위가 체액으로 가득차면 평소보다 더 튀어나올 수 있습니다.
위험/이점
혈액투석의 잠재적 위험이나 합병증은 무엇입니까?
어떤 사람들은 AV 누공이나 이식편에 문제가 있습니다. 감염, 혈류 불량, 흉터 조직이나 혈전으로 인한 막힘이 발생할 수 있습니다.
드물게 투석 중에 투석 바늘이 팔에서 빠지거나 튜브가 기계 밖으로 나오는 경우도 있습니다. 혈액 누출 감지 시스템은 귀하 또는 의료진에게 이 문제를 경고합니다. 누군가 문제를 해결할 때까지 기계는 일시적으로 꺼집니다. 이 시스템은 출혈로부터 당신을 보호합니다.
복막투석의 잠재적 위험이나 합병증은 무엇입니까?
어떤 사람들은 카테터 주변에 피부 감염이 발생합니다. 또한 박테리아가 카테터를 통해 복부 안으로 들어갈 때 발생하는 감염인 복막염에 걸릴 위험이 있습니다. 발열, 복통, 메스꺼움, 구토 등이 나타날 수 있습니다.
복부 카테터를 사용하고 배에 액체를 가득 채우는 것은 시간이 지남에 따라 복부 근육을 약화시킬 수 있습니다. 탈장이 발생할 수 있습니다. 이 상태는 소장과 같은 기관이 복부 근육을 뚫고 나올 때 발생합니다. 배꼽 근처나 복부와 허벅지 위쪽 사이의 사타구니 부위에 부풀어오르는 느낌이 들 수 있습니다. 의사는 수술을 통해 탈장을 치료할 수 있습니다.
복막 투석 중에 신체는 투석액에서 설탕인 포도당을 흡수합니다. 시간이 지남에 따라 이 여분의 설탕은 체중 증가로 이어질 수 있습니다.
회복과 전망
투석을 받는 사람의 전망(예후)은 어떻습니까?
투석을 하면 10~20년 정도 살 수 있다. 전망은 나이, 전반적인 건강 상태, 신부전 원인 및 기타 요인에 따라 달라집니다. 신장 이식을 받은 경우, 새 신장이 기능을 시작하면 투석을 중단할 수 있습니다.
투석을 받는 동안 활동이 제한되나요?
투석을 받고 있는 많은 사람들이 계속해서 일하고, 가족을 부양하고, 여행하면서 활동적인 삶을 살고 있습니다. 여행할 때 담당 의료 서비스 제공자가 귀하가 새 위치에 있는 센터에서 투석을 받을 수 있도록 도와드릴 수 있습니다. 두 가지 유형의 자가 투석을 수행하는 경우 투석액 가방과 휴대용 가정용 투석기(필요한 경우)를 가져갈 수 있습니다.
복막투석을 사용하는 사람들은 복부가 투석액으로 가득 차면 운동이나 특정 신체 활동을 제한해야 할 수도 있습니다. 그렇지 않은 경우 일반적으로 투석 환자에게 운동은 괜찮습니다. 특정 활동이나 스포츠 참여에 관해 담당 서비스 제공자에게 문의해야 합니다.
의사에게 전화해야 할 때
언제 의사에게 연락해야 하나요?
다음과 같은 증상이 나타나면 담당 의료 서비스 제공자에게 연락해야 합니다.
소변을 보기가 어렵습니다.
현기증, 실신, 비정상적인 갈증(탈수) 또는 기타 저혈압 징후.
메스꺼움과 구토.
AV 누공이나 카테터 부위의 발열, 진물, 발적과 같은 감염 징후.
심한 복통.
복부나 사타구니에 비정상적인 돌출(탈장)이 있습니다.
클리블랜드 클리닉의 메모
투석은 신부전이나 말기 신장 질환(ESRD) 환자의 생명을 구하는 치료법입니다. 무기한으로 투석을 계속할 수도 있고, 신장 이식을 받을 수 있을 때까지만 투석을 계속할 수도 있습니다. 투석에는 다양한 유형이 있습니다. 어떤 사람들은 집에서 투석하는 것을 선호하는 반면, 다른 사람들은 병원이나 투석 센터에 가기를 원합니다. 귀하의 의료 서비스 제공자는 귀하에게 가장 적합한 치료법을 찾기 위해 귀하와 함께 투석 옵션을 검토할 수 있습니다.
Dialysis
Dialysis is a treatment for individuals whose kidneys are failing. There are two types of dialysis, hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, that both perform normal kidney functions, filtering waste and excess fluid from the blood.ContentsOverviewProcedure DetailsRisks / BenefitsRecovery and OutlookWhen To Call the Doctor
ContentsOverviewProcedure DetailsRisks / BenefitsRecovery and OutlookWhen To Call the Doctor
Overview
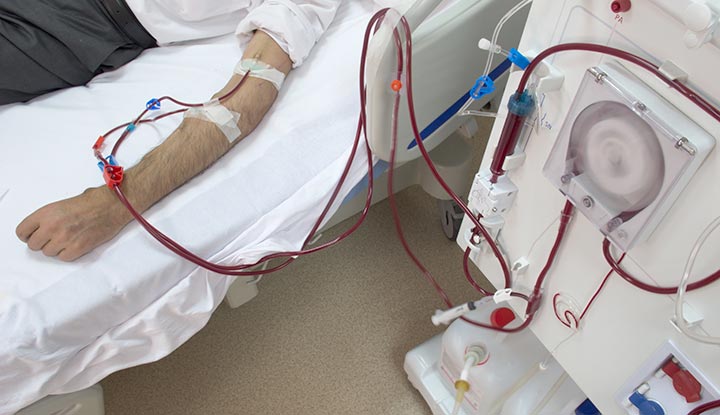
What is dialysis?
Dialysis is a treatment for people whose kidneys are failing. When you have kidney failure, your kidneys don’t filter blood the way they should. As a result, wastes and toxins build up in your bloodstream. Dialysis does the work of your kidneys, removing waste products and excess fluid from the blood.
Who needs dialysis?
People who have kidney failure, or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), may need dialysis. Injuries and conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes and lupus can damage kidneys, leading to kidney disease.
Some people develop kidney problems for no known reason. Kidney failure can be a long-term condition, or it can come on suddenly (acute) after a severe illness or injury. This type of kidney failure may go away as you recover.
There are five stages of kidney disease. In stage 5 kidney disease, healthcare providers consider you to be in end-stage renal disease (ESRD) or kidney failure. At this point, kidneys are carrying out around 10% to 15% of their normal function. You may need dialysis or a kidney transplant to stay alive. Some people undergo dialysis while waiting for a transplant.
What do the kidneys do?
Your kidneys are part of your urinary system. These two bean-shaped organs sit below your ribcage on each side of your spine. They clean toxins from your blood, returning filtered, nutrient-rich blood to the bloodstream.
The waste and extra water make urine, which moves from the kidneys into the bladder. Your kidneys also help regulate your blood pressure.
Procedure Details
What are the types of dialysis?
There are two ways to get dialysis:
- Hemodialysis.
- Peritoneal dialysis.
What is hemodialysis?
With hemodialysis, a machine removes blood from your body, filters it through a dialyzer (artificial kidney) and returns the cleaned blood to your body. This 3- to 5-hour process may take place in a hospital or a dialysis center three times a week.
You can also do hemodialysis at home. You may need at-home treatments four to seven times per week for fewer hours each session. You may choose to do home hemodialysis at night while you sleep.
What happens before hemodialysis?
Before you start hemodialysis, you’ll undergo a minor surgical procedure to make it easier to access the bloodstream. You may have:
- Arteriovenous fistula (AV fistula): A surgeon connects an artery and vein in your arm.
- Arteriovenous graft (AV graft): If the artery and vein are too short to connect, your surgeon will use a graft (soft, hollow tube) to connect the artery and vein.
AV fistulas and grafts enlarge the connected artery and vein, which makes dialysis access easier. They also help blood flow in and out of your body faster.
If dialysis needs to happen quickly, your provider may place a catheter (thin tube) into a vein in your neck, chest or leg for temporary access.
Your provider will teach you how to prevent infections in your fistula or graft. This provider will also show you how to do hemodialysis at home if you choose to do so.
What happens during hemodialysis?
During hemodialysis, the dialysis machine:
- Removes blood from a needle in your arm.
- Circulates the blood through the dialyzer filter, which moves waste into a dialysis solution. This cleansing liquid contains water, salt and other additives.
- Returns filtered blood to your body through a different needle in your arm.
- Monitors your blood pressure to adjust how fast blood flows in and out of your body.
What happens after hemodialysis?
Some people experience low blood pressure during or immediately after hemodialysis. You may feel nauseous, dizzy or faint.
Other side effects of hemodialysis include:
What is peritoneal dialysis?
With peritoneal dialysis, tiny blood vessels inside the abdominal lining (peritoneum) filter blood through the aid of a dialysis solution. This solution is a type of cleansing liquid that contains water, salt and other additives.
Peritoneal dialysis takes place at home. There are two ways to do this treatment:
- Automated peritoneal dialysis uses a machine called a cycler.
- Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) takes place manually.
What happens before peritoneal dialysis?
About three weeks before you start peritoneal dialysis, you’ll have a minor surgical procedure. A surgeon inserts a soft, thin tube (catheter) through your belly and into the peritoneum. This catheter stays in place permanently.
A healthcare provider will teach you how to perform peritoneal dialysis at home and prevent infections at the catheter site.
What happens during peritoneal dialysis?
During peritoneal dialysis, you:
- Connect the catheter to one branch of a Y-shaped tube. This tube connects to a bag that has dialysis solution. The solution flows through the tube and catheter into the peritoneal cavity.
- Disconnect the tube and catheter after about 10 minutes, when the bag is empty.
- Cap off the catheter.
- Go about your usual activities while the dialysis solution inside the peritoneal cavity absorbs waste and extra fluids from the body. This process can take 60 to 90 minutes.
- Remove the cap from the catheter and use the other branch of the Y-shaped tube to drain the fluid into a clean, empty bag.
- Repeat these steps up to four times a day. You sleep with the solution in your stomach all night.
Some people prefer to do peritoneal dialysis at night. With automated peritoneal dialysis, a machine called a cycler pumps the fluid in and out of the body while you sleep.
What happens after peritoneal dialysis?
The liquid in your belly can make you feel bloated or full. It might feel uncomfortable, but the treatment isn’t painful. Your stomach may stick out more than usual when it’s filled with fluid.
Risks / Benefits
What are the potential risks or complications of hemodialysis?
Some people have problems with the AV fistula or graft. You may develop an infection, poor blood flow or a blockage from scar tissue or a blood clot.
Rarely, the dialysis needle comes out of your arm, or a tube comes out of the machine, during dialysis. A blood leak detection system alerts you or the medical staff to this problem. The machine temporarily shuts off until someone fixes the problem. This system protects you from blood loss.
What are the potential risks or complications of peritoneal dialysis?
Some people develop skin infections around the catheter. You’re also at risk for peritonitis, an infection that occurs when bacteria get inside the abdomen through the catheter. You may experience fever, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
Using the abdominal catheter and pumping your belly full of fluid can weaken abdominal muscles over time. You may develop a hernia. This condition occurs when an organ like the small intestine pokes through the abdominal muscles. You may feel a bulge near the belly button or in the groin area between the abdomen and upper thigh. Your doctor can repair a hernia with surgery.
During peritoneal dialysis, your body absorbs dextrose, a sugar, from the dialysis solution. Over time, this extra sugar can lead to weight gain.
Recovery and Outlook
What’s the outlook (prognosis) for someone on dialysis?
It’s possible to live 10 to 20 years on dialysis. The outlook varies depending on your age, overall health, the cause of kidney failure and other factors. If you get a kidney transplant, you can stop dialysis when your new kidney starts working.
Will I have activity restrictions while I’m on dialysis?
Many people on dialysis continue to live active lives, working, raising families and traveling. When you travel, your healthcare provider can help arrange for you to get dialysis at a center at your new location. If you’re doing either type of self-dialysis, you can take dialysis solution bags and the portable home dialysis machine (if needed) with you.
People who use peritoneal dialysis may need to limit exercise or certain physical activities when the abdomen fills with dialysis solution. Otherwise, exercise is typically OK for people on dialysis. You should ask your provider about participating in specific activities or sports.
When To Call the Doctor
When should I call the doctor?
You should call your healthcare provider if you experience:
- Difficulty urinating.
- Dizziness, fainting, unusual thirst (dehydration) or other signs of low blood pressure.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Signs of infection, such as fever or oozing and redness at the AV fistula or catheter site.
- Severe abdominal pain.
- Unusual bulge in the abdomen or groin (hernia).
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Dialysis is a lifesaving treatment for people with kidney failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD). You may stay on dialysis indefinitely or just until you can get a kidney transplant. There are different types of dialysis. Some people prefer to do dialysis at home, while others want to go to a hospital or dialysis center. Your healthcare provider can review dialysis options with you to find the treatment that works best for you.










