목성의 대적반이 매우 이상하게 행동해 과학자들을 당혹스럽게 함
누르 알-시바이
2024년 10월 11일 금요일 오전 5시 4분 AEDT·2분 읽기
대불덩어리
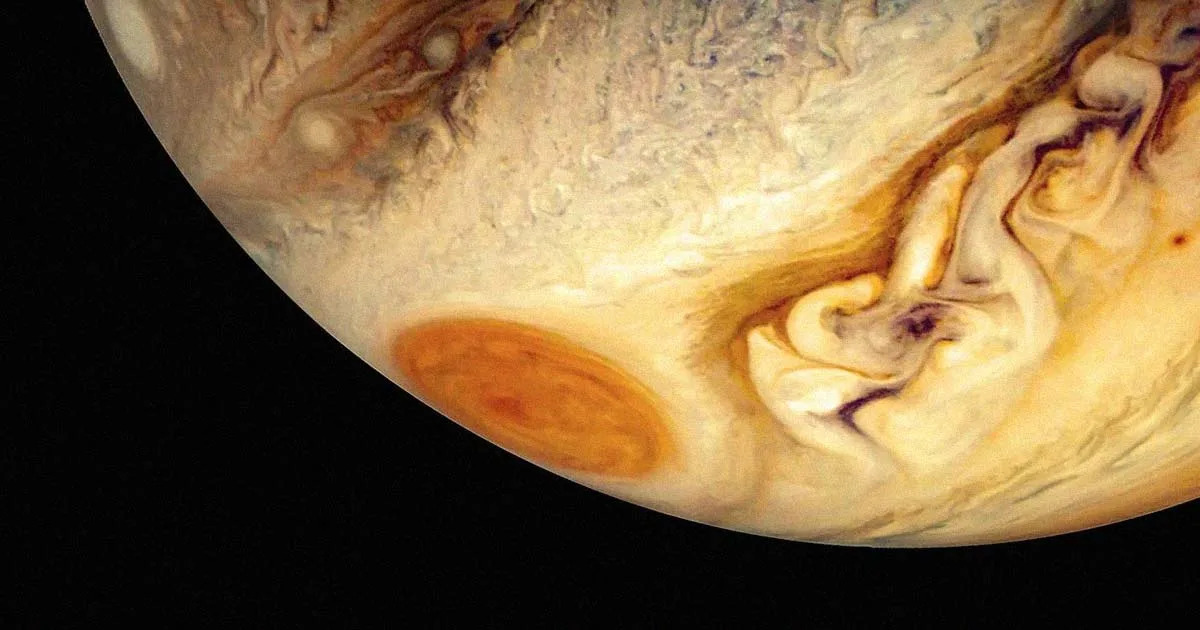
목성의 거대 적반(GRS)은 지구 전체를 삼킬 만큼 크고 허블의 새로운 이미지에서 알 수 있듯이 이전에 생각했던 것보다 훨씬 더 이상합니다.
허블 우주 망원경은 2023년 12월에서 2024년 3월 사이에 천문학자들을 오랫동안 매료시켜 온 거대하고 신비한 “반사이클론”을 자세히 살펴보았고, 크기가 계속 변할 뿐만 아니라 흔들리는 것처럼 보인다는 것을 발견했습니다.
“경도에 따라 운동이 약간씩 다르다는 것은 알고 있었지만 크기가 진동하는 것을 볼 줄은 예상하지 못했습니다.” NASA의 고다드 우주 비행 센터 소장인 에이미 사이먼이 성명을 통해 설명했습니다. “우리가 아는 한, 이전에는 확인되지 않았습니다.”
이 거대한 폭풍은 NASA가 지적했듯이 우리 태양계에서 가장 큰 폭풍입니다. 1979년 보이저 우주선은 지름이 무려 14,500마일에 달했지만, 최근 허블 관측에 따르면 10,250마일로 줄었습니다.
90일 동안 촬영한 이 최신 허블 이미지에 따르면 GRS는 스트레스 볼처럼 행동하는 듯합니다. 주변의 흰 구름은 마치 쥐는 손과 비슷합니다. 이 발견이 얼마나 매혹적인지 실감하게 해주는 놀라운 우연입니다.
Proper Look
Simon은 천문학자들이 수세기 동안 관찰했음에도 불구하고 GRS가 이 3개월간의 전담 관찰 이전에는 시간이 지남에 따라 반복적으로 이미지화된 적이 없다고 언급했습니다.
그녀는 “허블의 고해상도로 볼 때,” “GRS가 더 빠르고 느리게 움직이는 동시에 확실히 끼어들고 빠져나간다고 말할 수 있습니다.”라고 말했습니다.
그녀는 “매우 예상치 못한 일이었고, 현재로서는 유체 역학적 설명이 없습니다.”라고 덧붙였습니다.
Simon과 그녀의 팀의 발견은 지구의 허리케인을 연구하는 데에도 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
“GRS가 가속 및 감속할 때 북쪽과 남쪽의 바람이 강한 제트기류에 맞서고 있습니다.” 캘리포니아 대학교 버클리 캠퍼스의 새로운 연구 공동 연구자인 마이크 웡이 기관의 성명에서 설명했습니다. “이것은 가운데에 충전물이 너무 많으면 빵 조각이 튀어나오는 샌드위치와 비슷합니다.”
현재로서는 이 팀이 반점의 이상한 행동에 대한 가능한 설명을 여전히 조사하고 있지만, Simon의 팀은 이제 얼마나 이상한지 알게 되었으므로 눈 모양의 반점을 더 자세히 살펴볼 것입니다.
GRS에 대한 추가 정보: James Webb이 목성의 대적반 위의 신비한 구조물을 관찰
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot Is Acting Very Strangely, Puzzling Scientists
Noor Al-Sibai
Fri 11 October 2024 at 5:04 am AEDT·2-min read
Great Ball of Fire
Jupiter’s Giant Red Spot (GRS) is large enough to swallow the entire Earth — and as new imagery from Hubble suggests, it’s a lot weirder than previously thought.
Between December 2023 and March 2024, the Hubble Space Telescope took a closer look at the massive and mysterious “anticyclone” that has long fascinated astronomers and found that not only does its size keep changing, but that it appears to be, well, jiggling.
“While we knew its motion varies slightly in its longitude, we didn’t expect to see the size oscillate,” explained NASA’s Amy Simon, a director at the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center, in a statement. “As far as we know, it’s not been identified before.”
This ginormous storm is, as NASA points out, the largest in our Solar System. In 1979, the Voyager spacecraft clocked its diameter at a whopping 14,500 miles across — but per more recent Hubble observations, it’s shrunken to a mere 10,250 miles.
With these latest Hubble images taken over 90 days, the GRS seems to be behaving like a stress ball. The white clouds around it even sort of resemble a squeezing hand — an incredible coincidence that drives home how fascinating this finding really is.
Proper Look
Simon noted that despite having been observed by astronomers for centuries, the GRS had never been repeatedly imaged over time before this three-month dedicated look.
“With Hubble’s high resolution,” she said, “we can say that the GRS is definitively squeezing in and out at the same time as it moves faster and slower.“
“That was very unexpected, and at present, there are no hydrodynamic explanations,” she added.
Simon and her team’s findings could have implications for studying hurricanes on Earth as well.
“As it accelerates and decelerates, the GRS is pushing against the windy jet streams to the north and south of it,” explained Mike Wong, co-investigator of the new research from the University of California at Berkeley, in the agency’s statement. “It’s similar to a sandwich where the slices of bread are forced to bulge out when there’s too much filling in the middle.”
As of now, the team is still investigating possible explanations for the spot’s strange behavior — but we can be sure Simon’s team will be looking at the eye-shaped spot even closer now that they know how weird it is.
More on the GRS: James Webb Observes Mysterious Structures Above Jupiter’s Great Red Spot










