치매란?
치매는 기억력, 언어, 문제 해결 능력 및 일상 생활을 방해할 만큼 심각한 기타 사고 능력의 상실을 일반적으로 일컫는 말입니다. 알츠하이머병은 치매의 가장 흔한 원인입니다.
E-News를 구독하여 알츠하이머병의 영향을 받는 사람들을 돕는 방법을 알아보세요.
치매에 대하여
치매는 단일 질환이 아닙니다. 알츠하이머병을 포함한 다양한 질환을 앓고 있는 사람들이 경험할 수 있는 증상의 집합을 설명하는 포괄적인 용어입니다. 일반 용어인 “치매”로 그룹화된 질환은 비정상적인 뇌 변화로 인해 발생합니다. 치매 증상은 일상 생활과 독립적인 기능을 손상시킬 만큼 심각한 인지 능력이라고도 하는 사고 능력의 저하를 유발합니다. 또한 행동, 감정 및 관계에도 영향을 미칩니다.
알츠하이머병은 사례의 60-80%를 차지합니다. 뇌의 미세 출혈과 혈관 막힘으로 인해 발생하는 혈관성 치매는 치매의 두 번째로 흔한 원인입니다. 여러 유형의 치매로 인한 뇌 변화를 동시에 경험하는 사람들은 혼합형 치매를 앓고 있습니다. 갑상선 문제 및 비타민 결핍과 같이 가역적인 것을 포함하여 인지 장애 증상을 일으킬 수 있지만 치매가 아닌 다른 많은 상태가 있습니다.
치매는 종종 잘못해서 “노쇠” 또는 “노인성 치매”라고 불리는데, 이는 심각한 정신적 쇠퇴가 노화의 정상적인 부분이라는 이전에 널리 퍼져 있었지만 잘못된 믿음을 반영합니다.
자세히 알아보기: 일반적인 치매 유형, 알츠하이머병이란?
10가지 징후 알아보기
일반적인 연령 관련 기억 상실이 알츠하이머병 및 기타 치매의 초기 징후와 어떻게 다른지 알아보세요.징후 알아보기
인지 장애 및 치매의 증상 및 징후
기억 상실 또는 기타 인지 능력 상실의 초기 단계를 경미한 인지 장애(MCI)라고 합니다. 치매로 진행될 수 있는 MCI의 징후는 매우 다양할 수 있습니다. 다음과 같은 문제가 있습니다.
단기 기억.
지갑이나 지갑을 추적합니다.
청구서 지불.
식사 계획 및 준비.
약속 기억.
동네 밖으로 여행.
치매 증상은 점진적으로 진행되므로 인지 장애의 징후는 천천히 시작되어 시간이 지남에 따라 점차 악화되어 치매로 이어집니다. 본인이나 아는 사람이 기억 장애 또는 사고 능력의 다른 변화를 겪고 있다면 무시하지 마세요. 원인을 파악하기 위해 곧 의사를 만나세요. 전문적인 평가를 통해 치료 가능한 상태를 발견할 수 있습니다. 증상이 치매를 시사하더라도 조기 진단을 통해 개인은 이용 가능한 치료법에서 최대한의 이점을 얻을 수 있으며 임상 시험이나 연구에 자원할 수 있는 기회를 제공합니다. 또한 미래를 계획할 시간도 제공합니다.
자세히 알아보기: 알츠하이머병의 10가지 경고 신호, 단계
원인
치매는 뇌 세포에 손상을 입히는 다양한 질병으로 인해 발생합니다. 이러한 손상은 뇌 세포가 서로 통신하는 능력을 방해합니다. 뇌 세포가 정상적으로 통신할 수 없으면 사고, 행동 및 감정에 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
뇌에는 여러 개의 별개의 영역이 있으며 각각 다른 기능(예: 기억, 판단 및 운동)을 담당합니다. 특정 영역의 세포가 손상되면 해당 영역은 정상적으로 기능을 수행할 수 없습니다.
무료 e러닝 과정 수강
알츠하이머병과 치매 이해는 알츠하이머병과 치매의 차이, 증상, 단계, 위험 요인 등을 설명합니다. 과정 수강 다양한 유형의 치매는 뇌의 특정 영역에서 특정 유형의 뇌 세포 손상과 관련이 있습니다. 예를 들어, 알츠하이머병의 경우 뇌 세포 내부와 외부의 특정 단백질 수치가 높으면 뇌 세포가 건강을 유지하고 서로 소통하기 어렵습니다. 해마라고 하는 뇌 영역은 뇌의 학습과 기억의 중심이며, 이 영역의 뇌 세포가 가장 먼저 손상되는 경우가 많습니다. 그렇기 때문에 기억 상실은 종종 알츠하이머병의 가장 초기 증상 중 하나입니다.
치매를 유발하는 뇌의 대부분의 변화는 영구적이며 시간이 지남에 따라 악화되지만, 다음 상태로 인한 사고 및 기억 문제는 상태를 치료하거나 해결하면 개선될 수 있습니다.
우울증.
약물 부작용.
과도한 알코올 사용.
갑상선 문제.
비타민 결핍.
치매 진단
누군가가 치매인지 아닌지 판단하는 검사는 없습니다. 의사는 주의 깊은 병력, 신체 검사, 실험실 검사, 각 유형과 관련된 사고방식, 일상 기능 및 행동의 특징적인 변화를 바탕으로 알츠하이머병 및 기타 유형의 치매를 진단합니다. 의사는 높은 수준의 확신으로 사람이 치매인지 판단할 수 있습니다. 그러나 다른 치매의 증상과 뇌 변화가 겹칠 수 있기 때문에 정확한 유형의 치매를 판단하는 것은 더 어렵습니다. 어떤 경우에는 의사가 “치매”를 진단하고 유형을 지정하지 않을 수 있습니다. 이런 경우 s를 봐야 할 수 있습니다.
신경과 의사, 정신과 의사, 심리학자 또는 노인과 의사와 같은 전문의에게 문의하세요.
자세히 알아보기: 기억력 검사
치매 도움과 지원 제공
본인이나 아는 사람이 알츠하이머병이나 다른 치매 진단을 받았다면 혼자가 아닙니다. 알츠하이머 협회는 정보, 교육, 추천 및 지원을 제공하는 가장 신뢰할 수 있는 리소스 중 하나입니다.
24시간 연중무휴 헬프라인으로 전화하세요: 800.272.3900
알츠하이머병 및 치매 간병인을 위한 간병 정보 보기
지역사회의 지원 그룹 찾기
알츠하이머병과 싸우기 위해 기부하세요
알츠하이머병의 첫 생존자가 세상에 있지만, 여러분 없이는 우리가 거기에 도달할 수 없습니다. 지금 기부하세요
치매 치료 및 관리
궁극적으로 치매에 대한 효과적인 새로운 치료법으로 가는 길은 연구 자금 증가와 임상 연구 참여 증가를 통해 이루어집니다. 지금 당장 알츠하이머병과 다른 치매에 대한 임상 연구와 시험에 참여할 자원봉사자가 절실히 필요합니다.
자세히 알아보기: 기억 상실 치료제, 알츠하이머병에 대한 대체 치료법
치매 위험 및 예방
발견을 위한 스프린트
새로운 연구에 따르면 경미한 인지 장애와 치매의 위험을 줄이기 위해 할 수 있는 일이 있습니다. Carrillo 박사의 블로그 읽기 나이와 유전과 같은 치매의 일부 위험 요소는 변경할 수 없습니다. 그러나 연구자들은 다른 위험 요소가 뇌 건강과 치매 예방에 미치는 영향을 계속 탐구하고 있습니다.
2019년 알츠하이머 협회 국제 컨퍼런스®에서 보고된 연구에 따르면 건강한 식단, 금연, 규칙적인 운동 및 인지 자극을 포함한 여러 가지 건강한 라이프스타일 선택을 채택하면 인지 저하 및 치매의 위험을 줄일 수 있다고 합니다.
자세히 알아보기: 뇌 건강
What Is Dementia?
Dementia is a general term for loss of memory, language, problem-solving and other thinking abilities that are severe enough to interfere with daily life. Alzheimer’s is the most common cause of dementia.
Subscribe to E-News to learn how you can help those affected by Alzheimer’s.
About dementia
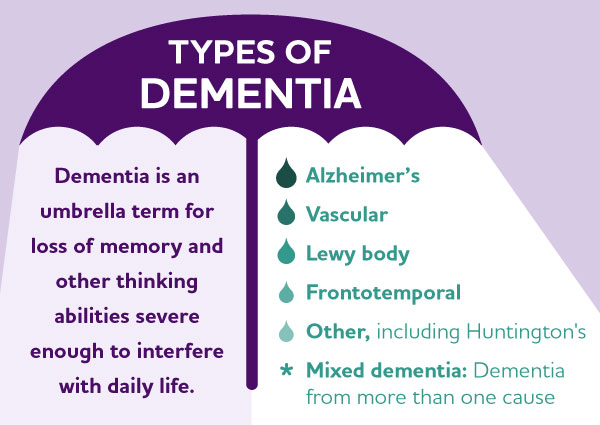 Dementia is not a single disease. It’s an overall term to describe a collection of symptoms that one may experience if they are living with a variety of diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease. Diseases grouped under the general term “dementia” are caused by abnormal brain changes. Dementia symptoms trigger a decline in thinking skills, also known as cognitive abilities, severe enough to impair daily life and independent function. They also affect behavior, feelings and relationships.
Dementia is not a single disease. It’s an overall term to describe a collection of symptoms that one may experience if they are living with a variety of diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease. Diseases grouped under the general term “dementia” are caused by abnormal brain changes. Dementia symptoms trigger a decline in thinking skills, also known as cognitive abilities, severe enough to impair daily life and independent function. They also affect behavior, feelings and relationships.
Alzheimer’s disease accounts for 60-80% of cases. Vascular dementia, which occurs because of microscopic bleeding and blood vessel blockage in the brain, is the second most common cause of dementia. Those who experience the brain changes of multiple types of dementia simultaneously have mixed dementia. There are many other conditions that can cause symptoms of cognitive impairment but that aren’t dementia, including some that are reversible, such as thyroid problems and vitamin deficiencies.
Dementia is often incorrectly referred to as “senility” or “senile dementia,” which reflects the formerly widespread but incorrect belief that serious mental decline is a normal part of aging.
Learn more: Common Types of Dementia, What is Alzheimer’s?
Know the 10 signs
Find out how typical age-related memory loss compares to early signs of Alzheimer’s and other dementias.Learn the Signs
Symptoms and signs of cognitive impairment and dementia
An early stage of memory loss or other cognitive ability loss is called mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Signs of MCI, which can progress to dementia, can vary greatly. Examples include problems with:
- Short-term memory.
- Keeping track of a purse or wallet.
- Paying bills.
- Planning and preparing meals.
- Remembering appointments.
- Traveling out of the neighborhood.
Dementia symptoms are progressive, which means that the signs of cognitive impairment start out slowly and gradually get worse over time, leading to dementia. If you or someone you know is experiencing memory difficulties or other changes in thinking skills, don’t ignore them. See a doctor soon to determine the cause. Professional evaluation may detect a treatable condition. And even if symptoms suggest dementia, early diagnosis allows a person to get the maximum benefit from available treatments and provides an opportunity to volunteer for clinical trials or studies.It also provides time to plan for the future.
Learn more: 10 Warning Signs, Stages of Alzheimer’s
Causes
Dementia is caused by a variety of diseases that cause damage to brain cells. This damage interferes with the ability of brain cells to communicate with each other. When brain cells cannot communicate normally, thinking, behavior and feelings can be affected.
The brain has many distinct regions, each of which is responsible for different functions (for example, memory, judgment and movement). When cells in a particular region are damaged, that region cannot carry out its functions normally.
Take our free e-learning course
Understanding Alzheimer’s and Dementia outlines the difference between Alzheimer’s and dementia, symptoms, stages, risk factors and more.Take the CourseDifferent types of dementia are associated with particular types of brain cell damage in particular regions of the brain. For example, in Alzheimer’s disease, high levels of certain proteins inside and outside brain cells make it hard for brain cells to stay healthy and to communicate with each other. The brain region called the hippocampus is the center of learning and memory in the brain, and the brain cells in this region are often the first to be damaged. That’s why memory loss is often one of the earliest symptoms of Alzheimer’s.
While most changes in the brain that cause dementia are permanent and worsen over time, thinking and memory problems caused by the following conditions may improve when the condition is treated or addressed:
- Depression.
- Medication side effects.
- Excess use of alcohol.
- Thyroid problems.
- Vitamin deficiencies.
Diagnosis of dementia
There is no one test to determine if someone has dementia. Doctors diagnose Alzheimer’s and other types of dementia based on a careful medical history, a physical examination, laboratory tests, and the characteristic changes in thinking, day-to-day function and behavior associated with each type. Doctors can determine that a person has dementia with a high level of certainty. But it’s harder to determine the exact type of dementia because the symptoms and brain changes of different dementias can overlap. In some cases, a doctor may diagnose “dementia” and not specify a type. If this occurs, it may be necessary to see a specialist such as a neurologist, psychiatrist, psychologist or geriatrician.
Learn more: Memory Tests
Dementia help and support are available
If you or someone you know has been diagnosed with Alzheimer’s or another dementia, you are not alone. The Alzheimer’s Association is one of the most trusted resources for information, education, referral and support.
- Call our 24/7 Helpline: 800.272.3900
- See our caregiving information for Alzheimer’s and dementia caregivers
- Locate a support group in your community
Donate to fight Alzheimer’s
The first survivor of Alzheimer’s is out there, but we won’t get there without you.Donate Now
Dementia treatment and care
Ultimately, the path to effective new treatments for dementia is through increased research funding and increased participation in clinical studies. Right now, volunteers are urgently needed to participate in clinical studies and trials about Alzheimer’s and other dementias.
Learn more: Medications for Memory Loss, Alternative Treatments for Alzheimer’s
Dementia risk and prevention
Sprint for Discovery
New research shows there are things we can do to reduce the risk of mild cognitive impairment and dementia.Read Dr. Carrillo’s BlogSome risk factors for dementia, such as age and genetics, cannot be changed. But researchers continue to explore the impact of other risk factors on brain health and prevention of dementia.
Research reported at the 2019 Alzheimer’s Association International Conference® suggests that adopting multiple healthy lifestyle choices, including healthy diet, not smoking, regular exercise and cognitive stimulation, may decrease the risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
Learn more: Brain Health










