혈압 차트: 범위 및 가이드
혈압을 관리하면 심장마비나 뇌졸중과 같은 심각한 건강 문제의 위험을 줄이는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 혈압 차트는 사람들이 자신의 혈압을 이해하고 변경이 필요한지 여부를 이해하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
혈압과 정상 및 비정상 수치에 대한 자세한 내용을 보려면 계속 읽으십시오.
혈압이란 무엇입니까?
혈압은 심장이 혈액을 펌핑할 때 혈액이 혈관벽에 가하는 힘을 말합니다. 의료 전문가는 혈압을 수은 밀리미터(mmHg) 단위로 측정합니다.
의사는 혈압을 개인의 심장 건강을 나타내는 지표로 사용할 수 있습니다. 고혈압이 있는 사람은 심장 문제가 발생하고 혈관벽이 손상될 위험이 있습니다.
낮은 혈압(또는 저혈압)은 건강이 좋다는 신호이지만 심각한 감염과 같은 특정 상황에서는 비정상적일 수 있습니다.
혈압이 너무 낮아지면 현기증이나 현기증을 느낄 수 있으며, 극단적인 경우에는 장기로 가는 혈류가 손상될 수 있습니다.
심한 저혈압은 산소가 풍부한 혈액의 손실로 인해 장기 손상 및 실신의 위험을 증가시킬 수 있습니다.
일반적으로 알코올과 염분 섭취를 제한하는 건강한 식단을 통해 건강한 체중을 유지하고 규칙적으로 운동함으로써 혈압을 정상 범위로 유지할 수 있습니다. 혈압에 문제가 있는 경우 의사는 혈압 조절에 도움이 되는 약물을 처방할 수 있습니다.
수축기 대 확장기
혈압 수치에는 두 개의 숫자가 있습니다. 사람들은 종종 이를 상한(수축기) 수치와 하한(이완기) 수치라고 부릅니다.
수축기 수치는 판독값에서 가장 높은 숫자이며 더 높은 수치입니다. 확장기는 낮은 숫자입니다.
고혈압이나 저혈압을 예방하려면 이 수치를 정상 범위 내로 유지해야 합니다. 아래에서는 수축기 및 확장기 판독값의 건강한 범위에 대해 설명합니다.
의료 자원
무료 콜레스테롤 낮추는 방법 — 모두 의학적으로 검토됨
콜레스테롤 수치를 관리하기 위해 지속적인 생활 방식 변화를 만드는 데 도움이 되는 콜레스테롤 세부 수업을 받으세요. 우리 전문가들은 콜레스테롤을 낮추는 팁을 매주 무료 5분 수업으로 모았습니다.
건강한 범위
미국심장협회에 따르면 건강한 혈압 범위는 다음과 같습니다.
수축기: 120 미만
확장기: 80 미만
사람이 다음과 같은 숫자를 가지고 있다면 혈압이 낮은 것입니다:
수축기: 90 이하
확장기: 60 이하
저혈압은 운동선수와 젊은 사람들에게 특히 흔합니다.
측정값이 다음과 같은 경우 혈압이 상승한 것입니다.
수축기: 120–129
확장기: 80 미만
혈압이 높은 사람은 아직 고혈압이 아니며 고혈압으로의 진행을 예방하는 데 도움이 되는 조치를 취할 수 있습니다.
작업에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
나트륨 섭취 줄이기
더 자주 운동하기
체중 감량
수면 무호흡증과 같은 원인이 될 수 있는 다른 질환 치료
알코올 섭취 제한
혈압을 표적으로 하는 약물 복용
고혈압의 3단계는 다음과 같습니다.
스테이지 1
2단계
위기
1단계 고혈압에서 숫자의 범위는 다음과 같습니다.
수축기: 130–139 또는
확장기: 80~89
2단계 고혈압에서 숫자의 범위는 다음과 같습니다.
수축기: 140 이상 또는
확장기: 90 이상
마지막으로 고혈압 위기가 있는 사람의 경우 숫자는 다음과 같습니다.
수축기: 180 이상
확장기: 120 이상
이 숫자는 성인용입니다. 연령, 체중, 성별이 모두 이러한 수치에 영향을 미칠 수 있으므로 부모나 보호자는 어린이의 건강한 범위에 대해 담당 의사와 상담해야 합니다.
고혈압의 위험
고혈압이 있는 사람은 혈압이 너무 높습니다.
고혈압이 있는 사람은 다음과 같은 질환이 발생할 위험이 높습니다.
관상 동맥 경화증
심부전으로 인해 다리가 붓고 체중이 증가하며 숨이 가빠집니다.
신장 기능 장애 또는 부전
확장기 기능 장애 또는 심장 근육의 경직
뇌졸중
대동맥박리, 관상동맥박리, 혈관박리
대 동맥류
시력 문제
기억력 문제
말초 동맥 질환
대부분의 경우 고혈압 증상은 없습니다.
그러나 혈압 상승으로 인해 고혈압 위기를 겪고 있는 사람은 다음과 같은 증상을 경험할 수 있습니다.
말하기 어려움
가슴 통증
허리 통증
시력 변화 또는 흐릿한 시력
폐의 체액으로 인한 호흡 곤란
무감각 또는 약점
두통
이러한 증상이 나타나는 사람은 누구나 즉시 치료를 받아야 합니다.
저혈압의 위험
심한 저혈압이 있는 사람은 혈압이 너무 낮습니다.
많은 의사들이 혈압을 낮추는 것의 중요성을 종종 강조하지만, 누군가의 혈압이 너무 낮을 수도 있습니다.
혈압이 매우 낮은 사람들은 다음과 같은 증상을 경험할 수 있습니다.
기절
현기증/현기증
메스꺼움
심장 두근거림
피로
흐릿한 시야
넘어짐으로 인한 부상 또는 의식 상실
심한 경우 장기 손상
이전
언급
사람들의 혈압은 부분적으로 다음과 같이 통제할 수 없는 요인들로 인해 발생합니다.
나이
섹스
가족력
만성 신장 질환
그러나 고혈압을 예방하기 위해 취할 수 있는 조치도 많이 있습니다. 여기에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
과일, 야채, 저지방 단백질, 복합 탄수화물을 포함하는 건강에 좋은 식단 섭취
규칙적인 운동, 특히 걷기, 자전거 타기 또는 달리기와 같은 심장 강화 운동
담배를 피우지 않는다
알코올 소비 제한
가공식품 섭취 제한
나트륨 섭취량을 하루 2g 미만으로 제한
수면 무호흡증 치료
당뇨병 관리 및 조절
과체중인 경우 체중 감량
스트레스를 줄이기 위한 조치를 취하기
의사를 만나야 할 때
심각한 고혈압 증상이 나타나면 심각한 합병증을 예방하기 위해 즉시 치료를 받아야 합니다.
또한 의사나 기타 의료 전문가의 검진 시 정기적으로 혈압 측정값을 받아야 합니다.
그러나 일반 혈압계를 사용하여 집에서 혈압을 측정할 수도 있습니다. 혈압 판독기에 혈압이 높거나 낮은 것으로 나타나면 의사와 상담해야 합니다.
혈압 모니터는 약국과 온라인에서 구입할 수 있습니다.
요약
혈압은 사람의 심장 건강을 나타내는 하나의 지표입니다. 압력이 너무 높으면 심각한 건강상의 합병증과 사망으로 이어질 수 있습니다.
혈압 상승의 모든 원인을 예방할 수 있는 것은 아니지만 생활 방식을 관리하고 고혈압 발병 위험 요소를 최소화함으로써 합병증의 위험을 줄일 수 있습니다.
고혈압이나 저혈압이 걱정되는 사람은 누구나 의사와 상담해야 합니다.
2019년 11월 21일에 마지막으로 의학적으로 검토됨
심장병고혈압공중 건강혈액/혈액학
이 기사를 검토한 방법:
소스
이 기사를 공유하세요
Payal Kohli 박사, MD, FACC의 의학 검토 — 2019년 11월 21일 Jenna Fletcher 작성
최근 뉴스
진동하고 섭취 가능한 캡슐이 비만 치료에 도움이 될 수 있습니까?
지나치게 낙관적인 태도는 잘못된 의사결정으로 이어질 수 있습니다.
단식 모방 다이어트란 무엇이며 심혈관 건강에 어떻게 도움이 됩니까?
추운 날씨에 달리는 것의 이점은 따뜻한 날씨에 달리는 것보다 더 큽니다.
명절 디저트: Great British Bake Off 레시피는 건강에 해롭나요?
정상적인 혈압 수치는 무엇입니까?
혈압이란 무엇입니까?
범위
기능
측정
방지
저혈압
테이크아웃
정상적인 혈압은 개인마다 다를 수 있지만 미국심장협회에서는 목표 혈압을 수축기 120mmHg, 이완기 80mmHg 미만으로 권장합니다.
1단계 고혈압은 사람의 수축기 혈압이 130~139이거나 확장기 혈압이 80~89일 때입니다.
그러나 혈압은 위험할 정도로 높아질 수도 있고 너무 낮아질 수도 있습니다.
이 기사에서는 혈압이 무엇인지, 어떻게 측정하는지, 그리고 측정이 우리의 건강에 어떤 의미를 갖는지 논의할 것입니다.
혈압이란 무엇입니까?
혈압은 순환계를 통해 혈액을 이동시키는 힘입니다. 혈압 없이 조직과 기관에 영양을 공급하기 위해 산소와 영양소가 순환계 주위로 밀려나지 않기 때문에 이는 중요한 힘입니다.
혈압은 또한 면역을 위한 백혈구와 항체, 인슐린과 같은 호르몬을 전달하기 때문에 매우 중요합니다.
산소와 영양분을 공급하는 것만큼 중요한 것은 전달되는 신선한 혈액은 우리가 숨을 쉴 때마다 내쉬는 이산화탄소와 간과 신장을 통해 제거되는 독소를 포함하여 신진 대사의 독성 폐기물을 제거할 수 있다는 것입니다.
혈액 자체는 온도를 포함하여 여러 가지 다른 속성을 가지고 있습니다. 또한 조직 손상에 대한 방어 수단 중 하나인 부상 후 혈액 손실을 방지하는 응고 혈소판을 운반합니다.
그러면 혈액이 동맥에 압력을 가하는 원인은 정확히 무엇입니까? 대답의 일부는 간단합니다. 심장은 심장이 박동할 때마다 수축할 때 혈액을 강제로 내보내 혈압을 생성합니다. 그러나 혈압은 심장 박동만으로는 생성될 수 없습니다.
정상 혈압 측정 범위
국립보건원(National Institutes of Health)과 미국심장협회(AHA)는 정상 혈압이 수축기 혈압 120mmHg, 확장기 혈압 80mmHg 미만이라고 언급합니다. 그러나 혈압은 여러 가지 이유로 자연스럽게 변합니다.
이전 2003년 지침 신뢰할 수 있는 소스에서는 혈압이 115/75mmHg를 초과하는 경우 20/10mmHg가 상승할 때마다 심혈관 질환 위험이 두 배로 증가한다고 밝혔습니다.
고혈압에 대한 전체 지침은 2017년 11월에 업데이트되었습니다. 이는 조기 개입을 허용합니다.
2017년부터 AHA는 고혈압 환자에게 140/90mmHg가 아닌 130/80mmHg로 치료를 받아야 한다고 권고했습니다.
그들은 또한 120-139/80-89mmHg 사이의 “고혈압 전단계” 범주를 삭제했습니다. 140/90mmHg의 혈압 측정값은 이제 예전처럼 1단계가 아닌 2단계 고혈압으로 분류됩니다.
이 카테고리는 이제 tw를 형성합니다.
o 별도의 범위:
혈압 상승(120-129/80mmHg 미만)
1기 고혈압, 130-139/80-89 mm Hg
고혈압 차트
범주 수축기 및/또는 확장기
정상 < 120mmHg 및 < 80mmHg 상승(위험 또는 고혈압 전단계) 120-129mmHg 및 < 80mmHg 고혈압 1단계 130-139mmHg 또는 80-89mmHg 고혈압 2단계 > 140mmHg 또는 > 90mmHg
고혈압 위기(긴급 상황) > 180mmHg 및/또는 > 120mmHg
이 새로운 지침에서 AHA는 또한 의사가 이전에 심장마비나 뇌졸중을 앓은 경우 또는 연령, 당뇨병 진단 또는 만성 신장 질환과 같은 이러한 상태에 대한 위험 요소가 있는 경우에만 약물을 처방해야 한다고 조언합니다.
고혈압 초기 단계의 치료는 주로 생활 방식의 변화를 통해 이루어져야 합니다.
의료 자원
무료 콜레스테롤 낮추는 방법 — 모두 의학적으로 검토됨
콜레스테롤 수치를 관리하기 위해 지속적인 생활 방식 변화를 만드는 데 도움이 되는 콜레스테롤 세부 수업을 받으세요. 우리 전문가들은 콜레스테롤을 낮추는 팁을 매주 무료 5분 수업으로 모았습니다.
신체에서 혈압의 기능
순환은 매우 정교한 형태의 배관과 유사합니다. 혈액에는 “흐름”이 있고 동맥은 “파이프”입니다. 기본 물리학 법칙에 따라 혈류가 발생하며 이 법칙은 정원용 호스 파이프에도 적용됩니다.
압력의 차이로 인해 혈액이 몸 전체를 통해 흐릅니다.
혈압은 심장에서 대동맥으로 들어가는 여정이 시작될 때 가장 높으며, 점차 작아지는 동맥 가지를 따라 가는 여정이 끝날 때 가장 낮습니다. 그 압력 차이로 인해 혈액이 흐르게 됩니다.
동맥은 수압에 영향을 미치는 정원 호스 파이프의 물리적 특성과 유사한 방식으로 혈압에 영향을 미칩니다. 파이프를 수축시키면 수축 지점의 압력이 증가합니다.
예를 들어, 동맥 벽의 탄력성이 없으면 혈액의 압력은 심장에서 펌핑될 때 더 빨리 떨어질 것입니다.
심장이 최대 압력을 생성하는 동안 동맥의 특성은 압력을 유지하고 혈액이 몸 전체로 흐르도록 하는 데에도 마찬가지로 중요합니다.
동맥의 상태는 혈압과 혈류에 영향을 미치며, 동맥이 좁아지면 결국 공급이 완전히 차단되어 뇌졸중, 심장마비 등 위험한 상태로 이어질 수 있습니다.
혈압 측정
혈압을 측정하는 데 사용되는 장치는 혈압계입니다. 고무 완장(손이나 기계 펌프로 팽창시키는 커프)으로 구성됩니다.
커프가 맥박을 멈출 만큼 팽창되면 전자적으로 또는 아날로그 다이얼을 통해 판독값이 판독됩니다.
판독값은 중력에 대항하여 튜브 주위로 수은을 이동시키는 데 걸리는 압력으로 표현됩니다. 이것이 바로 수은 밀리미터 단위(mmHg로 약칭)를 사용하여 압력을 측정하는 이유입니다.
혈압 측정은 일반적으로 통증이나 불편함을 유발하지 않습니다. 그러나 일시적으로 팔 주위가 조이는 느낌을 받을 수 있습니다.
혈압 수치
청진기는 맥박음이 돌아오는 정확한 지점을 식별하고 커프의 압력을 천천히 풀어줍니다. 청진기를 사용하면 혈압을 측정하는 사람이 두 가지 특정 지점을 들을 수 있습니다.
혈압 측정값은 두 가지 숫자로 구성됩니다. 첫 번째는 수축기 혈압이고 두 번째는 확장기 혈압입니다. 판독값은 예를 들어 90mmHg에 대해 140으로 표시됩니다.
수축기 혈압은 심장 수축으로 인해 발생하는 더 높은 수치이고, 확장기 혈압은 심장 박동 사이의 짧은 “휴식” 기간 동안 동맥의 더 낮은 압력입니다.
고혈압 예방을 위한 팁
AH신뢰할 수 있는 출처에는 건강한 혈압을 유지하기 위해 환자가 취할 수 있는 다음과 같은 조치가 나열되어 있습니다.
의사의 권고에 따라 건강한 체중을 유지하십시오.
과일과 채소가 풍부한 균형 잡힌 식단을 섭취하세요.
식단에서 나트륨, 즉 소금 섭취를 줄이세요.
가능하면 일주일 내내 하루에 최소 30분 동안 빠르게 걷기 등의 신체 활동을 정기적으로 하십시오.
스트레스를 관리하세요.
적당한 알코올 섭취. 남성은 하루에 두 잔 미만의 알코올 음료를 마셔야 합니다. 체중이 낮은 여성과 남성은 하루에 최대 한 잔의 알코올 음료를 섭취해야 합니다.
담배를 끊으.
의사와 협력하여 모든 처방을 적절하게 관리하십시오.
이러한 조치를 취하면 향후 건강 문제의 위험을 더욱 줄일 수 있습니다.
저혈압 우려
저혈압 또는 저혈압은 일반적으로 고혈압만큼 걱정스럽지 않습니다. 그러나 여전히 건강 문제를 나타낼 수 있습니다.
혈압 수치가 90/60mmHg 미만인 사람은 저혈압으로 간주됩니다. AH신뢰할 수 있는 소식통은 다른 증상이 동반되지 않는 한 의사는 일반적으로 이를 문제로 간주하지 않는다고 밝혔습니다.
이러한 근본적인 문제에는 내부 출혈, 심장병, 임신, 일부 약물 등이 포함될 수 있습니다.
사람이 ot를 경험하는 경우
증상이 나타나면 의사와 상담하여 근본적인 상태를 해결해야 합니다.
테이크아웃
혈압은 신체에 필수적입니다. 그러나 너무 높거나 너무 낮아질 수 있습니다. 혈압 수치가 너무 높은 것을 고혈압 또는 고혈압이라고 합니다. 이는 여러 가지 건강 문제를 일으킬 수 있으므로 의사와 함께 모니터링해야 합니다.
특히 조기 개입과 일부 생활 방식 조정을 통해 고혈압을 관리할 수 있습니다.
최종 의학 검토일: 2022년 3월 18일
고혈압혈액/혈액학심혈관/심장학
이 기사를 검토한 방법:
소스
이 기사를 공유하세요
Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.D., MSN의 의학 검토 — Markus MacGill 작성 — 2023년 1월 3일에 업데이트됨
최근 뉴스
진동하고 섭취 가능한 캡슐이 비만 치료에 도움이 될 수 있습니까?
지나치게 낙관적인 태도는 잘못된 의사결정으로 이어질 수 있습니다.
단식 모방 다이어트란 무엇이며 심혈관 건강에 어떻게 도움이 됩니까?
추운 날씨에 달리는 것의 이점은 따뜻한 날씨에 달리는 것보다 더 큽니다.
명절 디저트: Great British Bake Off 레시피는 건강에 해롭나요?
이 글이 도움 되었나요?
예
아니요
혈압에서 확장기와 수축기는 무엇입니까?
정의
확장기 대 수축기
건강한 범위
비정상 범위
요약
확장기 및 수축기는 심장 근육이 이완되고 수축되는 시기를 나타냅니다. 확장기 혈압과 수축기 혈압 사이의 균형이 사람의 혈압을 결정합니다. 혈압 수치에는 수축기 혈압과 이완기 혈압이 표시됩니다.
심장은 신체의 모든 조직과 기관에 산소가 풍부한 혈액을 공급하는 펌프입니다. 심장 박동은 심장 근육이 이완되고 수축되면서 발생합니다.
이 주기 동안 이완 기간을 확장기, 수축 기간을 수축기라고 합니다.
이 기사에서는 확장기 및 수축기가 혈압과 어떤 관련이 있는지 설명합니다. 또한 고혈압(고혈압) 및 저혈압(저혈압)과 관련된 위험 요인 및 합병증과 함께 정상 혈압이 무엇인지 논의합니다.
확장기 및 수축기 란 무엇입니까?
확장기는 심장 근육이 이완되는 때이고 수축기는 심장 근육이 수축하는 때입니다.
확장기는 다음과 같은 특징으로 정의됩니다.
확장기는 심장 근육이 이완되는 때입니다.
심장이 이완되면 심방이 혈액으로 채워지고 혈압이 감소합니다.
수축기는 다음과 같은 특징으로 정의됩니다.
수축기는 심장 근육이 수축하는 때입니다.
심장이 수축하면 혈액이 심장 밖으로 순환계의 큰 혈관으로 밀려납니다. 여기에서 혈액은 신체의 모든 장기와 조직으로 이동합니다.
수축기 동안 사람의 혈압이 증가합니다.
차이점
심장은 4개의 방으로 구성된 펌프입니다. 가운데는 오른쪽과 왼쪽으로 나누어져 있고, 각 측면은 위쪽과 아래쪽의 두 개의 방으로 더 나누어져 있습니다.
심방이라고 불리는 심장의 위쪽 두 방은 심장으로 들어오는 혈액을 받습니다. 아래쪽 두 개의 방을 심실이라고 합니다. 그들은 심장에서 신체의 나머지 부분으로 혈액을 펌핑합니다.
신체 주위로 혈액을 펌프질하기 위해 심장은 심장 주기라고 불리는 주기를 반복하여 수축했다가 이완합니다. 주기는 두 개의 심방이 수축하여 혈액을 심실로 밀어낼 때 시작됩니다. 그러면 심실이 수축하여 혈액을 심장 밖으로 밀어냅니다.
신체에서 심장의 오른쪽으로 되돌아오는 산소가 제거된 혈액은 폐를 통해 펌핑되어 산소를 얻습니다. 산소가 공급된 혈액은 심장의 왼쪽으로 이동하여 신체의 나머지 부분으로 펌핑됩니다.
확장기와 수축기는 다음과 같이 사람의 혈압에 다르게 영향을 미칩니다.
수축기 동안 심장이 혈액을 몸 전체로 밀면 혈관에 가해지는 압력이 증가합니다. 이것을 수축기 혈압이라고 합니다.
심장이 박동 사이에 이완되고 혈액이 다시 채워지면 혈압이 떨어집니다. 이것을 확장기 혈압이라고 합니다.
건강한 혈압이란 무엇입니까?
정상 혈압은 120/80mmHg 미만입니다.
혈압 결과를 받으면 확장기 및 수축기 측정값을 나타내는 두 개의 숫자가 표시됩니다. 이러한 측정값은 수은 밀리미터(mmHg)로 표시됩니다.
첫 번째 숫자는 수축기 혈압이고 두 번째 숫자는 이완기 혈압입니다.
미국심장학회(ACC)의 2017년 업데이트 지침에 따르면 현재 혈압 범주는 다음과 같습니다.
정상혈압 : 120/80mmHg 이하
혈압 상승: 수축기 혈압 120-129, 이완기 혈압 80 미만
1단계 고혈압: 수축기 혈압 130~139 또는 확장기 혈압 80~89mmHg
2단계 고혈압: 수축기 혈압이 140 이상이거나 이완기 혈압이 90mmHg 이상인 경우
이러한 업데이트된 지침은 미국인의 46%를 고혈압 범주에 포함시킬 가능성이 높습니다.
혈압은 항상 환자가 쉴 때와 며칠에 걸쳐 측정됩니다. 그 측정치
jeungsang-i natanamyeon uisawa sa
혈압 수치라고도 합니다.
고혈압과 저혈압
사람의 혈압은 여러 가지 이유로 너무 높거나 너무 낮을 수 있습니다. 고혈압과 저혈압 모두 치료하지 않으면 건강에 심각한 결과를 초래할 수 있습니다.
고혈압
성별과 연령에 따라 고혈압 위험이 높아질 수 있습니다.
고혈압 또는 고혈압은 사람이 혈관벽에 비정상적으로 높은 압력을 갖는 경우입니다. 이 상태는 수년에 걸쳐 점차적으로 발생하며 종종 증상이 없기 때문에 오랫동안 눈에 띄지 않을 수 있습니다.
다음 위험 요소는 고혈압 위험을 증가시킵니다.
나이. 혈압은 일반적으로 나이가 들수록 높아집니다.
성별. 남성은 55세 이전에 고혈압을 가질 가능성이 더 높지만, 여성은 55세 이후에 남성보다 고혈압을 가질 가능성이 더 높습니다.
경주. 고혈압은 백인이나 히스패닉계 미국인보다 아프리카계 미국인에게 더 흔합니다.
가족 역사. 가족 중 고혈압 환자가 있으면 장래에 고혈압이 발생할 위험이 높아집니다.
비만. 과체중이나 비만인 사람은 고혈압이 발생할 가능성이 더 높습니다. 이는 더 많은 양의 혈액이 혈관을 통해 순환하여 세포에 산소와 영양분을 공급하기 때문입니다. 혈액 순환이 더 많기 때문에 혈관 벽에 더 높은 압력이 가해집니다.
생활 습관. 신체 활동 부족, 흡연(간접 흡연 포함), 과도한 음주, 과도한 소금(나트륨) 섭취, 칼륨 섭취 부족, 스트레스 등이 위험을 증가시킬 수 있습니다.
특정 만성 질환. 신장 질환, 당뇨병, 수면 무호흡증은 고혈압의 위험을 증가시킬 수 있습니다.
임신. 어떤 경우에는 임신으로 인해 고혈압이 발생할 수 있습니다.
치료하지 않고 방치하면 고혈압은 합병증을 유발할 수 있으며 결국 다음과 같은 심각한 건강 문제를 일으킬 수 있습니다.
심장마비. 심장의 일부로 산소가 풍부한 혈액의 흐름이 차단되어 심장의 해당 부분이 산소를 공급받는 것을 방해합니다.
뇌졸중. 뇌졸중은 뇌로 가는 산소가 풍부한 혈액의 흐름이 차단되어 뇌의 해당 부분이 산소를 공급받지 못할 때 발생합니다.
심부전. 혈관에 가해지는 압력이 증가하여 심장이 신체의 요구 사항을 충족할 만큼 충분한 혈액을 공급하지 못하는 현상입니다.
말초 동맥 질환. 이는 심장이나 뇌, 가장 일반적으로 다리에 혈액을 공급하는 혈관 이외의 혈관이 좁아지는 현상입니다. 신체의 해당 부위로의 혈류가 영향을 받습니다.
동맥류. 동맥류는 혈관벽에 비정상적인 돌출이 발생하여 다른 기관을 압박하거나 혈류를 차단하거나 결국 파열될 수 있는 현상입니다.
만성 신장 질환. 신장 질환은 신장의 혈관이 좁아져 신장이 제대로 기능하지 못하여 발생할 수 있습니다.
저혈압
저혈압 또는 저혈압은 혈관벽의 혈압이 비정상적으로 낮을 때 발생합니다.
개인의 상태 발병 가능성을 높이는 위험 요소는 다음과 같습니다.
나이. 65신뢰할 수 있는 소스보다 나이가 많은 사람들은 일어설 때나 식사 후에 혈압 강하를 경험할 가능성이 더 높습니다. 어린이와 청소년은 현기증, 시야 흐림, 실신을 동반한 급격한 혈압 강하를 경험할 가능성이 더 높으며, 이는 신경 매개성 저혈압으로 알려져 있습니다.
특정 약물. 이뇨제를 포함한 고혈압 약은 저혈압을 유발할 수 있습니다.
특정 질병. 파킨슨병, 당뇨병, 일부 심장 질환과 같은 질환은 저혈압 위험을 증가시킵니다.
기타 요인. 임신, 더위 속에 서 있거나 장시간 가만히 서 있는 것도 저혈압을 유발할 수 있습니다.
경증 저혈압 환자는 피로, 실신 또는 현기증을 경험할 수 있습니다.
더 심각한 형태의 저혈압은 뇌를 포함한 신체의 주요 기관으로의 산소가 풍부한 혈류를 손상시킬 수 있습니다. 이런 일이 발생하면 사람은 졸리거나 혼란스럽거나 현기증을 느낄 수 있습니다. 심각한 경우에는 심장이나 뇌 손상으로 발전할 수 있습니다.
요약
확장기와 수축기는 심장 주기의 두 단계입니다. 이는 심장이 박동할 때 발생하며 신체의 모든 부분에 혈액을 운반하는 혈관 시스템을 통해 혈액을 펌핑합니다. 수축기는 심장이 혈액을 내보내기 위해 수축할 때 발생하고 확장기는 수축 후 심장이 이완될 때 발생합니다.
혈압이 높거나 낮다고 의심되는 사람은 의사와 상담하여 약물 치료나 생활 습관 변화 등 최선의 치료법을 찾아야 합니다.
혈압 문제로 인해 약을 복용하는 경우에도 혈압 수준을 정기적으로 측정해야 합니다. 그 이유는 해당 상태에 뚜렷한 증상이 없을 수도 있기 때문입니다.
2018년 4월 10일에 마지막으로 의학적으로 검토됨
혈액/혈액학심장혈관/심장학노인/노화
이 기사를 검토한 방법:
소스
이 기사를 공유하세요
ter Morales-Brown — 2023년 11월 16일에 업데이트됨
최근 뉴스
진동하고 섭취 가능한 캡슐이 비만 치료에 도움이 될 수 있습니까?
지나치게 낙관적인 태도는 잘못된 의사결정으로 이어질 수 있습니다.
단식 모방 다이어트란 무엇이며 심혈관 건강에 어떻게 도움이 됩니까?
추운 날씨에 달리는 것의 이점은 따뜻한 날씨에 달리는 것보다 더 큽니다.
명절 디저트: Great British Bake Off 레시피는 건강에 해롭나요?
이 글이 도움 되었나요?
예
아니요
저이완기 혈압이란 무엇이며 어떻게 관리하나요?
그것은 무엇입니까?
증상
원인
증가시키는 방법
진단
예방 및 관리
시야
요약
낮은 확장기 혈압은 심장 박동 사이의 혈압이 평소보다 낮은 경우입니다. 관리 방법은 전반적인 저혈압 관리와 동일합니다. 물을 더 많이 마시고 운동을 하는 것이 도움이 될 수 있는 두 가지 요령입니다.
이 기사에서는 원인, 증상 및 치료법을 포함하여 저확장기 혈압에 대해 자세히 살펴보겠습니다.
또한 의사가 상태를 진단하는 방법에 대해서도 논의하겠습니다.
마지막으로, 이 기사는 확장기 혈압이 낮은 사람들의 전망을 다루고 있습니다.
저확장기 혈압이란 무엇입니까?
Protonic Ltd/Stocksy
혈압 수치는 의사가 수은주 밀리미터(mmHg) 단위로 기록하는 두 가지 숫자를 사용합니다. 숫자는 수축기 혈압과 확장기 혈압을 측정합니다.
수축기 혈압은 가장 높은 수치이며 둘 중 더 높습니다. 심장이 박동할 때 혈액이 동맥벽에 가하는 압력의 정도를 측정합니다.
확장기 혈압은 낮은 숫자로, 심장이 박동 사이에 휴식을 취할 때 혈액이 동맥 벽에 가하는 압력을 나타냅니다.
혈압 측정값에는 수축기 혈압 수치가 먼저 표시되고 이완기 혈압 수치가 두 번째로 표시됩니다. 의사는 두 수치를 모두 고려하여 사람의 혈압을 평가합니다.
대부분의 성인의 경우 건강한 수치는 일반적으로 120/80mmHg 미만입니다. 저혈압 또는 저혈압은 90/60mmHg 미만의 혈압입니다.
저이완기 혈압 또는 단독 이완기 혈압은 수축기 혈압이 정상 수준으로 유지되는 동안 이완기 혈압이 60mmHg 미만으로 떨어지는 경우를 말합니다.
심장이 박동 사이에 쉬면 관상동맥은 산소가 풍부한 혈액을 심장에 공급합니다. 확장기 혈압이 너무 낮으면 심장은 필요한 혈액과 산소를 공급받지 못합니다. 이로 인해 시간이 지남에 따라 심장이 약해질 수 있습니다.
여기에서 혈압 측정값을 이해하는 방법에 대해 자세히 알아보세요.
증상
확장기 혈압이 낮은 사람은 어지러움과 피곤함을 느낄 수 있습니다. 또한 더 자주 넘어질 수도 있습니다. 이는 노인들에게 특히 위험할 수 있습니다.
일반적으로 저혈압은 아무런 문제를 일으키지 않습니다. 특정 한도 내에서는 저혈압이 있어도 건강할 수 있습니다. 다른 증상이 나타나면 저혈압이 문제가 됩니다.
현기증이 나는 느낌
기절
메스꺼움
탈수
착란
약한 느낌
흐릿한 시야
차갑고 축축하고 창백한 피부
빠르고 얕은 호흡
우울증
심계항진
두통
앉거나 휴식을 취하면 증상이 사라질 수 있습니다. 혈압이 너무 낮아지면 신체의 중요한 기관이 제대로 기능하는 데 충분한 영양분과 산소를 공급받지 못합니다. 이로 인해 신체가 쇼크 상태에 빠질 수 있습니다. 이런 일이 발생하면 즉시 의사의 진료를 받아야 합니다.
의료 자원
무료 콜레스테롤 낮추는 방법 — 모두 의학적으로 검토됨
콜레스테롤 수치를 관리하기 위해 지속적인 생활 방식 변화를 만드는 데 도움이 되는 콜레스테롤 세부 수업을 받으세요. 우리 전문가들은 콜레스테롤을 낮추는 팁을 매주 무료 5분 수업으로 모았습니다.
원인
노화로 인해 이완기 혈압이 낮아질 위험이 높아질 수 있습니다. 다른 위험 요인에는 항우울제, 이뇨제 또는 발기 부전 치료 약물과 같은 cTrusted SourceeTrusted Sourcertain 약물 복용이 포함됩니다.
고혈압 약을 복용하는 노인들은 이완기 혈압이 낮아질 위험이 더 높습니다.
어떤 사람들은 선천적으로 혈압이 낮아서 건강상의 문제를 일으키지 않습니다. 다른 사람들은 건강 문제로 인해 혈압 강하를 경험할 수도 있습니다. 이러한 문제에는 다음이 포함될 수 있습니다.
당뇨병
심장 질환
파킨슨 병
심각한 감염
빈혈증
알레르기 반응
어떤 사람들은 장기간 서 있으면 혈압이 떨어지는 신경 매개성 저혈압을 경험할 수도 있습니다.
저혈압은 다음으로 인해 발생할 수도 있습니다.
임신
장기간의 침대 휴식
출혈
탈수
술
누워 있다가 일어서면 혈압이 낮아질 수 있습니다. 이는 몇 초 동안만 지속될 수 있습니다.
일부 사람들에게는 식사 후에 혈압이 떨어지는 일이 발생할 수도 있습니다. Journal of Geriatric Cardiology에 따르면 이는 주로 노인, 고혈압 환자 또는 파킨슨병 환자에게서 발생합니다.
확장기 혈압을 높이는 방법
저확장기 혈압을 개선하는 데 도움이 되는 다음과 같은 다양한 치료 옵션이 있습니다.
특수
특정 약을 바꾸는 것에 대해 의사와 상담하기
혈액 순환을 개선하는 압축 스타킹 착용
혈액량을 증가시키고 탈수를 예방하기 위해 물을 마시십시오.
일시적으로 혈압을 높이기 위해 짠 음식을 더 많이 먹거나 카페인을 더 많이 마시는 것
의사는 특정 유형의 저혈압을 치료하기 위해 플루드로코르티손 및 미도드린과 같은 약물을 처방할 수 있습니다. 그러나 현재 저확장기 혈압을 치료할 수 있는 약은 없습니다.
진단
환자의 확장기 혈압이 낮은지 확인하기 위해 의사는 환자의 팔에 감는 장치인 혈압계를 사용하여 혈압을 측정합니다. 의사는 60mmHg 미만의 확장기 수치를 너무 낮은 것으로 간주합니다.
의사는 저혈압의 원인을 확인하기 위해 다음을 포함한 추가 검사를 수행할 수 있습니다.
혈액 또는 소변 검사
박동과 이상을 감지하기 위해 심장의 전기 신호를 읽는 심전도
심장의 상세한 영상을 보여주는 심장초음파검사
운동하는 동안 심장 모니터링을 받는 스트레스 테스트
환자가 자주 기절하는 경우, 의사는 기울기 테이블 테스트를 사용할 수 있습니다. 신체가 어떻게 반응하는지 확인하기 위해 테이블을 다양한 각도로 기울일 때 스트랩을 사용하여 테이블에 사람을 고정합니다.
예방 및 관리
나이가 낮은 이완기 혈압의 중요한 원인이 될 수 있다는 점을 고려하면, 이를 예방하는 것이 항상 가능한 것은 아닙니다. 그러나 건강한 체중을 유지하고, 균형 잡힌 식사를 하고, 규칙적으로 운동하는 것은 혈압 수준을 안정적으로 유지하는 데 도움이 될 뿐만 아니라 심장을 건강하게 유지하는 데도 도움이 됩니다.
확장기 혈압이 낮은 사람이 자신의 상태를 관리하기 위해 할 수 있는 몇 가지 생활 방식 변화가 있습니다.
담배를 끊다
알코올 소비 감소
적은 양의 식사하기
더 많은 물을 마시다
운동하다
오랫동안 앉거나 서 있지 않음
앉거나 누울 때 천천히 일어나기
시야
일반적으로 저혈압은 추가적인 건강 문제를 일으키지 않습니다. 그러나 낙상 위험이 높아질 수 있으며 이는 특히 노인에게 위험합니다.
확장기 혈압이 낮은 사람은 심부전 위험도 높을 수 있으므로 이를 최대한 잘 관리해야 합니다.
심부전의 증상은 다음과 같습니다.
호흡 곤란
지속적인 기침
하체에 붓기
피로
메스꺼움
착란
심계항진
이러한 증상 중 하나 이상을 경험하는 사람은 즉시 치료를 받아야 합니다.
요약
확장기 혈압은 심장 박동 사이에 혈액이 동맥벽에 가하는 압력을 측정합니다. 확장기 혈압이 낮으면 심장은 박동 사이에 산소가 풍부한 혈액을 덜 받습니다.
식이 요법, 운동 및 생활 방식의 변화는 모두 확장기 혈압을 높이는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
확장기 혈압이 낮은 사람은 정기적으로 의사를 방문해야 합니다. 이는 의사가 저혈압으로 인해 발생하는 새로운 문제를 신속하게 발견할 수 있도록 하기 위한 것입니다.
최종 의학 검토일: 2023년 1월 6일
혈액/혈액학심장혈관/심장학
이 기사를 검토한 방법:
소스
이 기사를 공유하세요
Megan Soliman, MD의 의학 검토 — Anna Smith Haghighi 작성 — 2023년 1월 11일에 업데이트됨
최근 뉴스
진동하고 섭취 가능한 캡슐이 비만 치료에 도움이 될 수 있습니까?
지나치게 낙관적인 태도는 잘못된 의사결정으로 이어질 수 있습니다.
단식 모방 다이어트란 무엇이며 심혈관 건강에 어떻게 도움이 됩니까?
추운 날씨에 달리는 것의 이점은 따뜻한 날씨에 달리는 것보다 더 큽니다.
명절 디저트: Great British Bake Off 레시피는 건강에 해롭나요?
이 글이 도움 되었나요?
예
아니요
혈압 수치 이해
수축기 및 확장기
혈압과 맥박
일반 독서
카테고리
의사 만나기
요약
혈압은 사람의 혈액이 동맥벽을 밀어내는 힘입니다. 사람의 혈압은 너무 낮아지거나 너무 높아질 수 있습니다. 너무 높으면 잠재적인 건강상의 합병증을 유발할 수 있습니다.
종종 사람들은 고혈압이나 고혈압의 증상을 경험하지 않습니다. 이는 특히 나이가 많거나 심장 합병증의 병력이 있는 경우 정기적으로 혈압을 검사하는 것이 중요하다는 것을 의미합니다.
고혈압은 또한 다음과 같은 다른 합병증을 유발할 수 있습니다.
눈 문제
뇌졸중
신부전
심장 질환
이 기사에서는 혈압 측정에 대해 사람이 알아야 할 모든 것과 그 의미를 설명합니다.
수축기 및 확장기
혈압이 너무 높으면 건강상의 합병증이 발생할 수 있습니다.
혈압 측정에는 혈액이 동맥벽에 가하는 압력의 양을 나타내는 두 가지 숫자가 포함됩니다.
수축기: 이것은 첫 번째 숫자입니다. 이는 심장이 수축할 때 혈액이 동맥 벽에 가하는 압력의 양을 나타냅니다.
확장기: 두 번째 숫자입니다. 이는 심장이 이완될 때 혈액이 동맥 벽에 가하는 압력의 양을 나타냅니다.
두 숫자 모두 다음에 대한 통찰력을 제공하므로 똑같이 중요합니다.
사람의 심장 건강에. 그러나 의사와 의료 전문가는 수축기 혈압을 일부 사람들의 심혈관 질환에 대한 주요 위험 요소로 간주하기 때문에 더 많은 관심을 기울이는 경우가 많습니다.
혈압과 맥박의 차이?
혈압은 동맥 벽에 부딪히는 혈액의 힘을 나타내는 반면, 맥박은 분당 심장이 뛰는 횟수를 나타냅니다.
안정시 심박수는 사람이 앉거나 누워 있거나 활동에 참여하지 않을 때를 말합니다.
활동성 심박수는 사람이 운동을 하거나 신체 활동을 하는 경우입니다.
모든 사람은 안정시 심박수가 약간 다르지만 평균 속도신뢰할 수 있는 소스는 분당 60~100비트입니다. 육체적으로 활동적인 사람의 심박수는 분당 40회 정도로 낮습니다.
혈압과 마찬가지로 사람의 심박수나 맥박은 심장이 얼마나 건강한지를 나타냅니다.
의료 자원
무료 콜레스테롤 낮추는 방법 — 모두 의학적으로 검토됨
콜레스테롤 수치를 관리하기 위해 지속적인 생활 방식 변화를 만드는 데 도움이 되는 콜레스테롤 세부 수업을 받으세요. 우리 전문가들은 콜레스테롤을 낮추는 팁을 매주 무료 5분 수업으로 모았습니다.
정상적인 독서란 무엇인가?
미국심장협회(AHA)에 따르면 정상적인 혈압 범위는 수은주 120/80밀리미터(mmHg)보다 낮습니다. 사람의 혈압이 정상 범위보다 높으면 혈압이 상승하거나 고혈압이 있을 수 있습니다.
사람의 혈압도 너무 낮게 떨어질 수 있습니다. 혈압이 정상보다 낮으면 건강 문제가 발생할 수도 있습니다.
너무 낮게 떨어지면 사람이 희미하거나 현기증이 나거나 어지러움을 느낄 수 있습니다. 지속적으로 낮은 수치를 나타내는 경우 의사와 상담해야 합니다.
혈압 카테고리
다섯 가지 카테고리가 있습니다. 혈압의 신뢰할 수 있는 출처:
정상 범위
AHA에 따르면 정상적인 혈압 수치는 120/80mmHg를 넘지 않습니다. 지속적으로 높은 숫자는 혈압이 높거나 고혈압이 있음을 의미할 수 있습니다.
높은 범위
혈압 범위 상승은 수축기 혈압이 120~129이고 이완기 혈압이 80 미만일 때 발생합니다.
혈압이 높은 사람은 혈압을 낮추기 위한 조치를 취하지 않으면 고혈압이 발생할 가능성이 더 높습니다.
고혈압: 1단계
1기 고혈압 환자의 혈압 수치는 지속적으로 수축기 130~139, 이완기 80~89입니다.
의사는 생활방식을 바꾸라고 조언하고 심장마비나 뇌졸중의 위험을 줄이기 위해 혈압약을 처방할 수도 있습니다.
고혈압: 2단계
2단계 고혈압이 있는 사람의 혈압 수치는 지속적으로 약 140/90mmHg 이상입니다.
혈압을 낮추는 데 도움이 되도록 혈압약을 복용하고 생활 방식을 바꿔야 할 가능성이 높습니다.
고혈압 위기
혈압이 갑자기 180/120mmHg로 측정되면 고혈압 위기가 발생합니다. 이런 일이 발생하면 5분 동안 기다렸다가 혈압을 다시 측정해야 합니다. 수치가 여전히 높으면 의사의 의학적 도움을 받으십시오.
판독값이 높으면 장기 손상을 경험할 수 있으며 다음과 같은 증상이 나타납니다.
호흡 곤란
무감각 또는 약점
시력의 변화
가슴 통증
허리 통증
말하기 어려움
이러한 증상이 나타나면 즉시 911에 전화해야 합니다.
의사를 만나야 할 때
누군가가 장기 부전의 징후와 함께 고혈압 위기를 겪고 있다면 응급 의료 지원을 받아야 합니다.
심장병, 심장 마비, 뇌졸중 또는 기타 심장 문제의 병력이 있는 사람은 정기적으로 의사를 만나 혈압 검사를 받아야 합니다. 또한 집에서 정기적으로 압력을 확인하고 싶을 수도 있습니다.
혈압이 정상 수치보다 높은 경우 원인과 치료 방법을 이해하기 위해 의사를 만나야 합니다.
요약
사람들은 심장이 수축하고 이완될 때 혈액이 동맥에 가하는 압력을 나타내는 두 가지 숫자를 사용하여 혈압을 측정합니다.
의사는 혈압 수치가 지속적으로 120/80 미만인 경우 혈압이 정상 범위에 있는 것으로 간주합니다.
수치가 높을수록 사람이 고혈압 또는 고혈압이 있음을 나타낼 수 있습니다. 치료하지 않고 방치하면 심장 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다.
혈압을 조절하는 데 도움이 되도록 식단과 운동 요법을 변경할 수 있습니다.
2019년 12월 3일에 마지막으로 의학적으로 검토됨
심장병혈액/혈액학심혈관/심장학
이 기사를 검토한 방법:
소스
이 기사를 공유하세요
Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI의 의학 검토 — 2019년 12월 3일 Jenna Fletcher 작성
최근 뉴스
진동하고 섭취 가능한 캡슐이 비만 치료에 도움이 될 수 있습니까?
지나치게 낙관적인 태도는 잘못된 의사결정으로 이어질 수 있습니다.
단식 모방 다이어트란 무엇이며 심혈관 건강에 어떻게 도움이 됩니까?
추운 날씨에 달리는 것의 이점은 따뜻한 날씨에 달리는 것보다 더 큽니다.
휴일 데
serts: Great British Bake Off 요리법은 건강에 해롭습니까?
이 글이 도움 되었나요?
예
아니요
55세 이전의 높은 콜레스테롤, 고혈압은 나중에 심장병의 위험을 증가시킵니다
전문가들은 젊은 성인의 혈압을 모니터링하는 것이 중요하다고 말합니다. 퓨즈/게티 이미지
연구자들은 55세 이전의 고혈압과 높은 콜레스테롤이 나중에 심장병의 위험을 증가시킬 수 있다고 보고합니다.
그들은 개인이 55세 이후에 이러한 상태를 통제하기 위한 조치를 취하더라도 이러한 위험은 여전히 남아 있다고 지적합니다.
연구진은 심장병은 일반적으로 유전적 요인을 포함한 위험 요인이 누적된 결과라고 말했습니다. 그러나 나이가 들수록 유전적 요인의 역할은 줄어듭니다.
55세 이전에 고혈압 및/또는 고콜레스테롤이 있는 경우, 나이가 들어감에 따라 이러한 상태가 호전되는 사람이라도 심장 질환의 위험이 높아질 수 있습니다.
이러한 발견은 오늘 PLOS ONE 저널에 발표된 연구의 일부입니다.
연구자들은 UK Biobank에 등록된 참가자에 대한 3-샘플 무작위 분석을 사용했습니다.
분석에는 세 그룹이 있었습니다.
136,648명의 사람들이 콜레스테롤(LDL-C)이 높았습니다.
135,431명의 사람들이 수축기 혈압(SBP)이 상승했습니다.
24,052명이 관상동맥심장병을 앓고 있었습니다.
연구자들이 심장병 연구를 통해 배운 것
연구진은 유전적 요인을 바탕으로 높은 LDL-C와 SBP를 예측할 수 있는 경우 진단 연령에 관계없이 관상동맥심장병의 위험이 있다는 점에 주목했습니다.
그들은 또한 초기 및 중년에 SBP 및 LDL-C가 상승한 사람들은 노년기의 SBP 및 LDL-C 수치와 관계없이 관상 동맥 심장 질환의 위험이 증가한다는 점을 지적했습니다.
연구원들은 또한 관상동맥 심장 질환은 일반적으로 SBD 및 LDL-C와 같은 위험 요인에 대한 누적 노출의 결과이며 이것이 개인의 위험에 장기간 영향을 미칠 수 있다고 지적했습니다.
그들은 관상 동맥 심장 질환에 대한 SBP의 영향이 나이가 들수록 감소한다고 덧붙였습니다. 이것은 이전 관찰로 인한 것일 수 있는 것이 아닙니다. 여러 질병에 대한 유전적 영향이 나중에 쇠퇴하기 시작한다는 것입니다.
연구 결과에 대한 토론에서 연구원들은 또한 그들의 연구 결과가 노년기에도 혈압약과 스타틴의 사용이 도움이 될 수 있음을 시사하는 무작위 대조 시험과 일치한다고 지적했습니다. 그럼에도 불구하고 스타틴과 혈압약의 사용은 나이가 들수록 감소하는 경우가 많다고 한다.
연구자들은 SBP 및/또는 LDL-C가 높은 젊은 개인을 치료하는 것이 평생 동안 누적된 노출을 최소화하는 데 필수적이라고 제안합니다.
“우리의 연구 결과는 노령만으로는 적절한 LDL-C 및 혈압 강하 치료를 보류할 이유가 되어서는 안 된다는 것을 시사합니다. 왜냐하면 유전적으로 매개된 LDL-C 및 SBP가 [관상동맥 심장 질환]의 사고 위험에 미치는 영향은 전체적으로 일관되기 때문입니다. 인생’이라고 적었다.
전문가들은 콜레스테롤과 고혈압 연구에 무게를 두고 있습니다
“우리는 고혈압과 높은 콜레스테롤이 심장 질환의 위험 요소라는 것을 알고 있습니다.”라고 캘리포니아 MemorialCare Saddleback Medical Center의 중재적 심장 전문의이자 구조적 심장 프로그램의 의료 책임자인 Cheng-Han Chen 박사는 말했습니다. 연구. “이 연구는 장기간에 걸쳐 관계를 조사하고 다양한 연령대의 관계에 대한 이해를 더해줍니다.”
Chen은 Medical News Today에 “나는 이미 평생 동안 고혈압과 고콜레스테롤을 치료하고 있으므로 환자를 대하는 방식은 바뀌지 않을 것입니다.”라고 말했습니다. “나는 이미 55세 미만의 고콜레스테롤과 고혈압 치료를 모두 받고 있습니다.”
이번 연구에 참여하지 않은 캘리포니아 주 오렌지 코스트 의료 센터(Orange Coast Medical Center)의 MemorialCare 심장 및 혈관 연구소의 심장 전문의이자 지질 전문의인 Yu-Ming Ni 박사는 이번 연구가 그의 전반적인 치료 범위를 바꾸지 않을 것이라는 데 동의합니다.
그러나 Ni는 더 어린 나이에 콜레스테롤 관리에 더 적극적일 수 있다고 말했습니다.
그는 메디컬 뉴스 투데이(Medical News Today)와의 인터뷰에서 “식단/생활 방식을 변경할 가능성이 더 많은 젊은 환자들과 이야기를 나누고, 위험에 대해 더 잘 설명하고, 그들이 일상 생활에서 할 수 있는 변화에 대해 협력할 수 있습니다.”라고 말했습니다.
“나이가 들수록 흡연, 앉아서 생활하는 생활방식, 나쁜 식습관 등 다른 요인들이 유전적 역할을 대신하게 됩니다.” Ni가 덧붙였습니다. “그런 일이 생기면 우리는 콜레스테롤 수치가 높아질 위험을 낮추기 위해 이러한 것들을 수정해야 합니다. 이 연구는 콜레스테롤 수치가 높은 기간이 길어질수록 심장병 발병 가능성이 높아진다는 것을 보여줍니다.”
Ni는 “나는 영국 바이오뱅크를 활용한 연구를 좋아합니다. 왜냐하면 그곳에서 끌어낼 수 있는 사람들이 많기 때문입니다”라고 말했습니다. “결과는 신뢰할 만하다.”
연구자들은 그들의 연구에 한계가 있다고 지적했습니다. 예를 들어, 항고혈압제와 지질강하제의 사용은 연령층에 따라 다양했습니다. 이를 설명하기 위해 연구자들은 치료 상태에 따라 SBP와 LDL-C를 조정했습니다.
의료 자원
무료 콜레스테롤 낮추는 방법 — 모두 의학적으로 검토됨
저녁 식사를 위해 콜레스테롤 마이크로 레슨 받기
콜레스테롤 수치를 관리하기 위해 지속적인 생활 방식 변화를 가져오십시오. 우리 전문가들은 콜레스테롤을 낮추는 팁을 매주 무료 5분 수업으로 모았습니다.
고혈압의 위험인자, 콜레스테롤
전문가들은 생활습관 요인이 높은 콜레스테롤과 혈압 모두에 중요한 역할을 한다고 말합니다.
질병통제예방센터(CDC)에 따르면 고혈압의 위험 요소 중 일부는 다음과 같습니다.
건강에 해로운 식단, 특히 나트륨 함량이 높고 칼륨 함량이 낮은 식단
신체 활동이 없음
비만
알코올의 오용
흡연 또는 기타 담배 사용
CDC신뢰할 수 있는 소스는 고콜레스테롤에 대한 위험 요소를 다음과 같이 나열합니다.
제2형 당뇨병
비만
포화지방과 트랜스지방이 많이 함유된 식단
신체 활동이 없음
흡연
열악한 식습관, 비만, 신체 활동 부족 및 흡연이 두 목록 모두에 있습니다.
콜레스테롤심장병고혈압
이 기사를 공유하세요
2023년 12월 20일 Eileen Bailey 작성 — Jill Seladi-Schulman 박사가 사실 확인
최근 뉴스
진동하고 섭취 가능한 캡슐이 비만 치료에 도움이 될 수 있습니까?
지나치게 낙관적인 태도는 잘못된 의사결정으로 이어질 수 있습니다.
단식 모방 다이어트란 무엇이며 심혈관 건강에 어떻게 도움이 됩니까?
추운 날씨에 달리는 것의 이점은 따뜻한 날씨에 달리는 것보다 더 큽니다.
명절 디저트: Great British Bake Off 레시피는 건강에 해롭나요?
이 글이 도움 되었나요?
예
아니요
뉴스레터 받기
건강 분야에서 새롭게 떠오르는 발전을 통해 끊임없이 변화하는 의학 세계를 따라가십시오.
이메일을 입력하세요
Suzanne Falck, M.D., FACP의 의학적인 검토 — By Pe
Managing blood pressure can help reduce the risk of serious health problems, such as heart attacks and stroke. Blood pressure charts can help people understand their blood pressure and if they need to make any changes.
Keep reading for more information about blood pressure and what are normal and abnormal readings.
What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure refers to the force that blood puts on the walls of the blood vessels as the heart pumps blood. Healthcare professionals measure blood pressure in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
Doctors can use blood pressure as an indicator of a person’s heart health. People with high blood pressure — or hypertension — are at risk of developing heart problems and damage to the walls of the blood vessels.
Low blood pressure — or hypotension — is a sign of good health, but can be abnormal in certain situations, such as during severe infection.
If blood pressure falls too low, it can cause people to feel dizzy or light-headed and, in extreme cases, can compromise blood flow to the organs.
Severe hypotension can increase the risk of organ damage and fainting due to the loss of oxygen-rich blood.
Typically, a person can keep their blood pressure in the normal range by maintaining a healthy weight through a healthful diet that limits alcohol and salt intake, and by exercising regularly. If they are having trouble with blood pressure, a doctor may be able to prescribe medication to help regulate it.
Systolic vs. diastolic
There are two numbers in a blood pressure reading. People often call these the upper (systolic) and lower (diastolic) numbers.
Systolic is the top number on the reading and is the higher one. Diastolic is the lower number.
A person should keep these numbers within the normal range to prevent either hypertension or hypotension. We describe the healthy ranges for systolic and diastolic readings below.

HEALTHLINE RESOURCE

Free Cholesterol-Lowering Tips — All Medically Reviewed
Get our cholesterol micro-lessons to support you in making lasting lifestyle changes to manage your cholesterol levels. Our experts have gathered cholesterol-lowering tips into free weekly 5-min lessons.
Healthy ranges
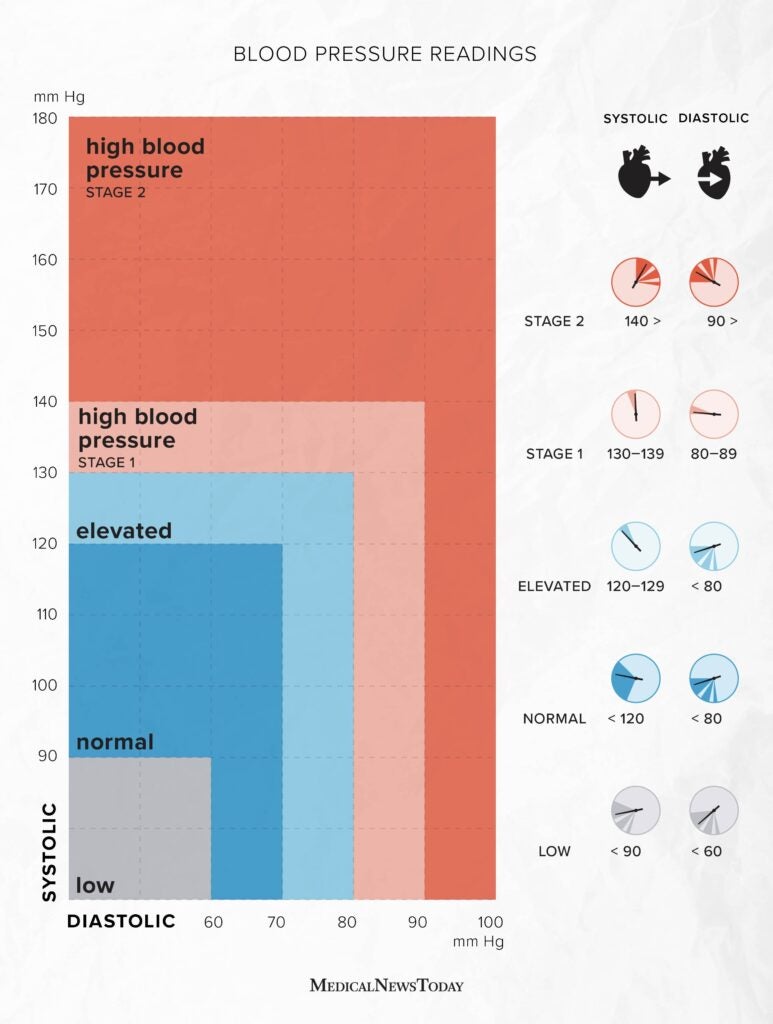
According to the American Heart AssociationTrusted Source, a healthy blood pressure range is:
- systolic: less than 120
- diastolic: less than 80
If a person has the following numbersTrusted Source, they have low blood pressure:
- systolic: 90 or below
- diastolic: 60 or below
Lower blood pressure is especially common in athletes and young people.
A person has elevated blood pressure if their readings are:
- systolic: 120–129
- diastolic: less than 80
A person with elevated blood pressure is not yet hypertensive and can take steps to help prevent progression to hypertension.
Actions include:
- reducing sodium intake
- exercising more frequently
- losing weight
- treating other conditions that may be contributing, such as sleep apnea
- limiting alcohol intake
- taking medications that target blood pressure
The three stages of hypertension are:
- stage 1
- stage 2
- crisis
In stage 1 hypertension, the numbers will range between:
- systolic: 130–139 or
- diastolic: 80–89
In stage 2 hypertension, the numbers will range between:
- systolic: 140 or higher or
- diastolic: 90 or higher
Finally, if a person has hypertension crisis, the numbers will read:
- systolic: 180 or higher
- diastolic: 120 or higher
These numbers are for adults. A parent or caregiver should talk to a child’s doctor about healthy ranges for children, as age, weight, and sex can all affect these numbers.
Risks of hypertension
If a person has hypertension, their blood pressure is too high.
When a person is hypertensive, they are at an increased risk of developing conditions, such as:
- coronary atherosclerosis
- heart failure, leading to swelling in the legs, weight gain, and shortness of breath
- kidney dysfunction or failure
- diastolic dysfunction, or stiffening of the heart muscle
- stroke
- aortic dissection, coronary dissection, vascular dissection
- aortic aneurysm
- vision issues
- memory problems
- peripheral arterial disease
In most cases, there are no symptoms of high blood pressure.
However, a person who is experiencing a hypertension crisis due to elevated blood pressure levels may experience the following symptoms:
- difficulty speaking
- chest pain
- back pain
- change in vision or blurry vision
- shortness of breath due to fluid in the lungs
- numbness or weakness
- headache
Anyone experiencing these symptoms should seek immediate medical treatment.
Risks of hypotension
When a person has severe hypotension, their blood pressure is too low.
Though many doctors often stress the importance of lowering blood pressure, it is possible for someone’s blood pressure to be too low.
People with very low blood pressure may experience the following symptoms:
- fainting
- dizziness/lightheadedness
- nausea
- heart palpitations
- fatigue
- blurry vision
- injury from falling or loss of consciousness
- organ damage in severe cases
Prevention
People’s blood pressure is partially due to factors they cannot control, such as:
- age
- sex
- family history
- chronic kidney disease
However, there are also many steps a person can take to prevent high blood pressure. These include:
- eating a healthful diet that includes fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and complex carbohydrates
- exercising regularly, particularly cardio workouts, such as walking, cycling, or running
- not smoking
- limiting alcohol consumption
- restricting consumption of processed foods
- limiting sodium intake to less than 2 grams daily
- treating sleep apnea
- managing and regulating diabetes
- reducing weight if overweight
- taking steps to reduce stress
When to see a doctor
If a person experiences any symptoms of critical hypertension, they should seek immediate medical attention to prevent serious complications.
A person should also receive regular blood pressure readings at check-ups with their doctor or other healthcare professionals.
However, a person can also take their blood pressure at home using an over-the-counter blood pressure monitor. If the blood pressure reader indicates a person has high or low blood pressure, they should talk to their doctor.
Blood pressure monitors are available in pharmacies and online.
Summary
Blood pressure is one indicator of a person’s heart health. If the pressure is too high, it can lead to serious health complications and potentially death.
Though not all causes of elevated blood pressure are preventable, a person can reduce their risk of complications by managing their lifestyle and minimizing risk factors for developing high blood pressure.
Anyone concerned about high or low blood pressure should speak to a doctor.
Last medically reviewed on November 21, 2019
How we reviewed this article:
SOURCES
Share this article

Medically reviewed by Dr. Payal Kohli, M.D., FACC — By Jenna Fletcher on November 21, 2019
Latest news
- Could a vibrating, ingestible capsule help treat obesity?
- Being overly optimistic may be linked to poor decision-making
- What is a fasting-mimicking diet, and how does it benefit cardiovascular health?
- Benefits of running in the cold outweigh warm weather running
- Holiday desserts: Are Great British Bake Off recipes unhealthy?
What is a normal blood pressure reading?
A normal blood pressure can vary between individuals, but the American Heart Association recommend a target blood pressure below 120 mm Hg systolic and 80 mm Hg diastolic.
Stage 1 hypertension is either when a person’s systolic pressure is 130–139Trusted Source or their diastolic pressure is 80–89.
However, blood pressure can become dangerously high, and it can also get too low.
In this article, we will discuss what blood pressure is, how it is measured, and what the measurements mean for our health.
What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure is the force that moves blood through the circulatory system. It is an important force because oxygen and nutrients would not be pushed around the circulatory system to nourish tissues and organs without blood pressure.
Blood pressure is also vital because it delivers white blood cells and antibodies for immunity and hormones such as insulin.
Just as important as providing oxygen and nutrients, the fresh blood that gets delivered is able to pick up the toxic waste products of metabolism, including the carbon dioxide we exhale with every breath and the toxins we clear through the liver and kidneys.
Blood itself carries a number of other properties, including its temperature. It also carries one of the defenses against tissue damage, the clotting platelets that prevent blood loss following injury.
But what exactly causes blood to exert pressure in the arteries? Part of the answer is simple — the heart creates blood pressure by forcing out blood when it contracts with every heartbeat. Blood pressure, however, cannot be created solely by a pumping heart.
Ranges of normal blood pressure readings
The National Institutes of HealthTrusted Source and the American Heart Association (AHA)Trusted Source cite normal blood pressure to be below 120 mm Hg systolic and 80 mm Hg diastolic. However, blood pressure changes naturally for many reasons.
Older 2003 guidelinesTrusted Source state that for blood pressures above a figure of 115/75 mm Hg, every rise of 20/10 mm Hg doubles the risk of cardiovascular disease.
The overall guidelines for high blood pressure received an updateTrusted Source in November 2017. They allow for earlier intervention.
Since 2017, the AHA has advised that people with high blood pressure should receive treatment at 130/80 mm Hg rather than 140/90 mm Hg.
They also removed the “prehypertension” category between 120-139/80-89 mm Hg. A blood pressure reading of 140/90 mm Hg now qualifies as stage II hypertension and not stage I, as it used to be.
This category now forms two separate ranges:
- elevated blood pressure, from 120-129/less than 80 mm Hg
- stage I hypertension, from 130-139/80-89 mm Hg
High blood pressure chart
| Category | Systolic | and/or | Diastolic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | < 120 mm Hg | and | < 80 mm Hg |
| Elevated (at risk, or prehypertension) | 120-129 mm Hg | and | < 80 mm Hg |
| Hypertension stage 1 | 130-139 mm Hg | or | 80-89 mm Hg |
| Hypertension stage 2 | > 140 mm Hg | or | > 90 mm Hg |
| Hypertensive crisis (emergency situation) | > 180 mm Hg | and/or | > 120 mm Hg |
In these new guidelines, the AHA also advises that doctors should only prescribe medication in cases of a previous heart attack or stroke, or in the presence of risk factors for these conditions, such as age, a diabetes diagnosis, or chronic kidney disease.
Treatment at the earlier stages of high blood pressure should instead come mainly through lifestyle changes.

HEALTHLINE RESOURCE

Free Cholesterol-Lowering Tips — All Medically Reviewed
Get our cholesterol micro-lessons to support you in making lasting lifestyle changes to manage your cholesterol levels. Our experts have gathered cholesterol-lowering tips into free weekly 5-min lessons.
The function of blood pressure in the body
Circulation is similar to a highly sophisticated form of plumbing — blood has “flow,” and arteries are “pipes.” A basic law of physics gives rise to blood flow, and this law also applies in a garden hose pipe.
Blood flows through the body because of a difference in pressure.
Blood pressure is highest at the start of its journey from the heart — when it enters the aorta — and it is lowest at the end of its journey along progressively smaller branches of arteries. That pressure difference is what causes blood to flow.
Arteries affect blood pressure in a similar way to the physical properties of a garden hose pipe affecting water pressure. Constricting the pipe increases pressure at the point of constriction.
Without the elastic nature of the artery walls, for example, the pressure of the blood would fall away more quickly as it is pumped from the heart.
While the heart creates the maximum pressure, the properties of the arteries are just as important to maintaining it and allowing blood to flow throughout the body.
The condition of the arteries affects blood pressure and flow, and narrowing of the arteries can eventually block the supply altogether, leading to dangerous conditions including stroke and heart attack.
Blood pressure measurement
The device used to measure blood pressure is a sphygmomanometer. It consists of a rubber armband — the cuff that is inflated by hand or machine pump.
Once the cuff is inflated enough to stop the pulse, a reading is taken either electronically or on an analog dial.
The reading is expressed in terms of the pressure it takes to move mercury around a tube against gravity. This is the reason for pressure being measured using the unit millimeters of mercury, abbreviated to mm Hg.
Measuring blood pressure typically does not cause any pain or discomfort. However, it can temporarily feel tight around the arm.
Blood pressure readings
A stethoscope identifies the precise point when the pulse sound returns, and the pressure of the cuff is slowly released. Using the stethoscope enables the person measuring the blood pressure to listen out for two specific points.
Blood pressure readings consist of two figures: The systolic pressure first and the diastolic pressure second. The reading is given as, for example, 140 over 90 mm Hg.
The systolic pressure is the higher figure caused by the heart’s contraction, while the diastolic number is the lower pressure in the arteries during the brief “resting” period between heartbeats.
Tips for preventing high blood pressure
The AHATrusted Source list the following measures patients can take to help keep a healthy blood pressure:
- Maintain a healthy body weight based on a doctor’s recommendation.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Cut down on sodium, or salt, in the diet.
- Regularly engage in physical activity, such as brisk walking, for at least 30 minutes a day, most days of the week, if possible.
- Manage stress.
- Moderate alcohol intake. Men should drink fewer than two alcoholic beverages a day. Women and men with a lower body weight should consume a maximum of one alcoholic drink a day.
- Quit smoking.
- Work with a doctor to manage all prescriptions properly.
Taking these steps can reduce the risk of health problems further down the line.
Low blood pressure concerns
Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is not typically as worrisome as high blood pressure. However, it can still indicate health issues.
A person with a blood pressure reading of less than 90/60 mm HgTrusted Source is considered to have low blood pressure. The AHATrusted Source has stated that doctors do not usually consider this a problem unless other symptoms exist alongside it.
These underlying issues could include internal bleeding, heart disease, pregnancy, some medications, among other situations.
If a person experiences other symptoms, they should speak with their doctor to address any underlying conditions.
Takeaway
Blood pressure is essential to the body. However, it can become too high or too low. A blood pressure reading that is too high is called hypertension, or high blood pressure. This can cause a number of health issues and should be monitored with a doctor.
High blood pressure can be managed, especially with early intervention and some lifestyle adjustments.
Last medically reviewed on March 18, 2022
How we reviewed this article:
SOURCES
Share this article

Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.D., MSN — By Markus MacGill — Updated on January 3, 2023
Latest news
- Could a vibrating, ingestible capsule help treat obesity?
- Being overly optimistic may be linked to poor decision-making
- What is a fasting-mimicking diet, and how does it benefit cardiovascular health?
- Benefits of running in the cold outweigh warm weather running
- Holiday desserts: Are Great British Bake Off recipes unhealthy?
Was this article helpful?
What are diastole and systole in blood pressure?
Diastole and systole refer to when the heart muscles relax and contract. The balance between diastolic and systolic pressure determines a person’s blood pressure. A blood pressure reading displays systolic and diastolic pressure.
The heart is a pump that supplies all tissues and organs of the body with oxygen-rich blood. The heartbeat is caused by the heart muscles relaxing and contracting.
During this cycle, the period of relaxation is called diastole and the period of contraction is called systole.
In this article, we will explain how diastole and systole relate to blood pressure. We also discuss what is normal blood pressure, along with risk factors and complications linked to high blood pressure (hypertension) and low blood pressure (hypotension).
What are diastole and systole?

Diastole is defined by the following characteristics:
- Diastole is when the heart muscle relaxes.
- When the heart relaxes, the chambers of the heart fill with blood, and a person’s blood pressure decreases.
Systole is defined by the following characteristics:
- Systole is when the heart muscle contracts.
- When the heart contracts, it pushes the blood out of the heart and into the large blood vessels of the circulatory system. From here, the blood goes to all of the organs and tissues of the body.
- During systole, a person’s blood pressure increases.
Differences
The heart is a pump composed of four chambers. It is divided in the middle into a right and left side, and each side is divided further into two chambers — the upper and lower chambers.
The two upper chambers of the heart called the atria receive the blood that is entering the heart. The two lower chambers are called the ventricles. They pump the blood out of the heart to the rest of the body.
To pump the blood around the body, the heart contracts and then relaxes over and over again in a cycle called the cardiac cycle. The cycle begins when the two atria contract, which pushes blood into the ventricles. Then, the ventricles contract, which forces the blood out of the heart.
The deoxygenated blood that comes back from the body to the right side of the heart is then pumped through the lungs where it picks up oxygen. The oxygenated blood then travels to the left side of the heart and is pumped to the rest of the body.
Diastole and systole affect a person’s blood pressure differently, as follows:
- When the heart pushes blood around the body during systole, the pressure placed on the vessels increases. This is called systolic pressure.
- When the heart relaxes between beats and refills with blood, the blood pressure drops. This is called diastolic pressure.
What is a healthy blood pressure?

When a person receives their blood pressure results, they will see two numbers that represent the diastole and systole measurements. These measurements are given as millimeters of mercury (mm Hg).
The first number is the systolic pressure and the second is the diastolic pressure.
According to the American College of Cardiology’s (ACC) updated 2017 guidelines, the current blood pressure categories are:
- Normal blood pressure: under 120/80 mmHg
- Elevated blood pressure: a systolic pressure of between 120-129 and a diastolic pressure of under 80
- Stage 1 hypertension: a systolic pressure of between 130-139 or a diastolic pressure of between 80 and 89 mmHg
- Stage 2 hypertension: a systolic pressure of at least 140 or a diastolic pressure of at least 90 mmHg
These updated guidelines are likely to place 46 percent of Americans in the category of having high blood pressure.
Blood pressure is always measured when the person is at rest and over several days. Its measurements are also called blood pressure readings.
High and low blood pressure
A person’s blood pressure can become too high or too low for many reasons. Both high and low blood pressure can cause serious health consequences if left untreated.
High blood pressure

High blood pressure or hypertension is when a person has abnormally high pressure against the walls of their blood vessels. This condition develops gradually over many years and may go unnoticed for a long time, as there are often no symptoms.
The following risk factors increase a person’s risk of high blood pressure:
- Age. Blood pressure is usually higher with age.
- Gender. Men are more likelyTrusted Source to have high blood pressure before the age of 55, but women are more likely than men to have the condition after the age of 55.
- Race. High blood pressure is more common in African Americans than Caucasian or Hispanic Americans.
- Family history. Having a family member with high blood pressure increases the risk of a person developing high blood pressure in the future.
- Obesity. A person who is overweight or obese is more likely to develop high blood pressure. This is because a higher volume of blood circulates through blood vessels to supply the cells with oxygen and nutrients. Because there is more blood circulating, there is a higher pressure on the vessel walls.
- Lifestyle habits. A lack of physical activity, smoking tobacco (including second-hand smoking), drinking too much alcohol, consuming too much salt (sodium) or too little potassium, and stress may increase the risk.
- Certain chronic conditions. Kidney disease, diabetes, and sleep apnea can increase the risk of high blood pressure.
- Pregnancy. In some cases, pregnancy can cause high blood pressure.
When left untreated, high blood pressure can cause complications and, eventually, serious health problems, such as:
- Heart attack. A block in the flow of oxygen-rich blood to a portion of the heart, preventing that portion of the heart from getting oxygen.
- Stroke. A stroke happens when there is a block in the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the brain, preventing that portion of the brain from getting oxygen.
- Heart failure. Failure of the heart to pump enough blood to meet the body’s demands, caused by the increased pressure on the vessels.
- Peripheral artery disease. This is the narrowing of blood vessels other than those that supply the heart or the brain, most commonly of the legs. Blood flow to that part of the body is affected.
- Aneurysm. An aneurysm is the development of an abnormal bulge in a blood vessel wall, which may press on other organs, block blood flow, or eventually burst.
- Chronic kidney disease. Kidney disease can be caused by narrowing of blood vessels in the kidneys, which prevents them from working properly.
Low blood pressure
Low blood pressure or hypotension occurs when a person has abnormally low blood pressure against the walls of their blood vessels.
Risk factors that increase a person’s chance of developing the condition include:
- Age. People older than 65Trusted Source are more likely to experience a drop in blood pressure while standing up, or after eating. Children and young people are more likely to experience a rapid drop in blood pressure accompanied by dizziness, blurred vision, and fainting, which is known as neurally mediated hypotension.
- Certain medications. High blood pressure medicines, including diuretics, can cause hypotension.
- Certain diseases. Conditions such as Parkinson’s, diabetes, and some heart conditions increase the risk of low blood pressure.
- Other factors. Pregnancy, standing in the heat, or standing still for long periods of time can also cause low blood pressure.
A person with mild low blood pressure may experience fatigue, fainting, or dizziness.
More severe forms of low blood pressure can compromise oxygen-rich blood flow to the body’s major organs, including the brain. If this happens, a person may feel sleepy, confused, or light-headed. In serious cases, this can evolve to heart or brain damage.
Summary
Diastole and systole are two phases of the cardiac cycle. They occur as the heart beats, pumping blood through a system of blood vessels that carry blood to every part of the body. Systole occurs when the heart contracts to pump blood out, and diastole occurs when the heart relaxes after contraction.
A person who suspects that they have high or low blood pressure should consult their doctor to find out the best treatments, which may include medications or lifestyle changes.
Even if a person is taking medication for problematic blood pressure, they should still measure their blood pressure levels regularly, since the condition may not have any apparent symptoms.
Last medically reviewed on April 10, 2018
How we reviewed this article:
SOURCES
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Suzanne Falck, M.D., FACP — By Peter Morales-Brown — Updated on November 16, 2023
Latest news
- Could a vibrating, ingestible capsule help treat obesity?
- Being overly optimistic may be linked to poor decision-making
- What is a fasting-mimicking diet, and how does it benefit cardiovascular health?
- Benefits of running in the cold outweigh warm weather running
- Holiday desserts: Are Great British Bake Off recipes unhealthy?
Was this article helpful?
What is low diastolic blood pressure and how to manage it
Low diastolic blood pressure is when blood pressure between heartbeats is lower than usual. Ways of managing it will be the same as for managing low blood pressure overall. Drinking more water and doing some exercise are two tips that may help.
This article will take a closer look at low diastolic blood pressure, including its causes, symptoms, and treatments.
We will also discuss how a doctor diagnoses the condition.
Finally, the article addresses the outlook for people with low diastolic blood pressure.
What is low diastolic blood pressure?

Blood pressure readings use two numbers that doctors record in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). The numbers measure systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure.
Systolic blood pressure is the top number and is the higher of the two. It measures how much pressure the blood applies to the artery walls when the heart beats.
Diastolic blood pressure is the lower number, which shows the pressure the blood applies to the artery walls when the heart rests between beats.
A blood pressure reading will show the systolic blood pressure number first and diastolic blood pressure second. A doctor will assess a person’s blood pressure by considering both numbers.
In most adults, a healthy reading is usually less than 120/80 mm HgTrusted Source. Low blood pressure, or hypotension, is blood pressure that is below 90/60 mm Hg.
Low diastolic blood pressure, or isolated diastolic blood pressure, is when the diastolic blood pressure falls below 60 mm Hg while the systolic blood pressure remains at a normal level.
When the heart rests between beats, the coronary arteries receive and supply the heart with oxygen-rich blood. If the diastolic pressure is too low, the heart will not get the blood and oxygen it needs. This may cause the heart to weaken over time.
Learn more about understanding blood pressure readings here.
Symptoms
A person who has low diastolic blood pressure may feel dizzy and tired. They may also fall more often. This can be particularly dangerous in older adults.
Usually, low blood pressure will not cause any issues. Within certain limits, it can be healthy to have low blood pressure. Low blood pressure becomes a problem when other symptoms are presentTrusted Source, such as:
- feeling lightheaded
- fainting
- nausea
- dehydration
- confusion
- feeling weak
- blurry vision
- cold, clammy, pale skin
- rapid, shallow breathing
- depression
- palpitations
- headache
Symptoms may subside when sitting down or resting. If blood pressure drops too low, the body’s vital organs will not get enough nutrients and oxygen to function correctly. This could lead to the body going into shock. If this happens, a person should immediately seek medical attention.

HEALTHLINE RESOURCE

Free Cholesterol-Lowering Tips — All Medically Reviewed
Get our cholesterol micro-lessons to support you in making lasting lifestyle changes to manage your cholesterol levels. Our experts have gathered cholesterol-lowering tips into free weekly 5-min lessons.
Causes
Aging can increase the risk of low diastolic blood pressure. Other risk factors include taking cTrusted SourceeTrusted Sourcertain medicationsTrusted Source, such as antidepressants, diuretics, or drugs to treat erectile dysfunction.
Older people who take medications for high blood pressure are at higher risk of experiencing lower diastolic blood pressure.
Some people naturally have lower blood pressure, which causes them no health problems. Other people may experience a drop in blood pressure due to an issue with their health. These issues can include:
- diabetes
- heart problems
- Parkinson’s disease
- severe infection
- anemia
- allergic reaction
Some people may also experience neurally mediated hypotension, where blood pressure drops after they have been standing for long periods.
Low blood pressure can also be due to:
- pregnancy
- prolonged bed rest
- bleeding
- dehydration
- alcohol
Moving from lying down to standing up can lead to a dip in blood pressure. This may only last for a few seconds.
A dip in blood pressure can also happen to some people after they eat a meal. According to the Journal of Geriatric CardiologyTrusted Source, this mostly occurs in older adults, those with high blood pressure, or people with Parkinson’s disease.
How to increase diastolic blood pressure
There are numerous treatment options that can help improve low diastolic blood pressure, such as:
- speaking with a doctor about changing certain medications
- wearing compression stockings, which improve circulation
- drinking water to increase blood volume and prevent dehydration
- eating more salty foods or drinking more caffeine to temporarily increase blood pressure
Doctors may prescribe drugs, such as fludrocortisone and midodrine, to treat certain kinds of low blood pressure. However, there are currently no medicines available to treat low diastolic blood pressure.
Diagnosis
To determine if a person has low diastolic blood pressure, a doctor will use a sphygmomanometer, a device that straps around the person’s arm, to take a blood pressure reading. A doctor will consider a diastolic reading below 60 mm Hg to be too low.
A doctor can carry out further tests to identify the cause of a person’s low blood pressure, including:
- blood or urine tests
- an electrocardiogram to read the heart’s electrical signals in order to detect the rhythm and any abnormalities
- an echocardiogram to show detailed images of the heart
- a stress test, where a person undergoes heart monitoring while exercising
If the person finds that they faint often, the doctor may use a tilt table test. They use straps to secure the person to the table as it is tilted at different angles to see how the body reacts.
Prevention and management
Given that age can be a significant cause of low diastolic blood pressure, it is not always possible for a person to prevent it. However, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and exercising regularly can help keep blood pressure levels stable, as well as help keep the heart healthy.
There are several lifestyle changes that someone with low diastolic blood pressure can make to manage their condition:
- stopping smoking
- lowering alcohol consumption
- eating smaller meals
- drinking more water
- exercising
- not sitting or standing still for long periods
- getting up slowly when sitting or lying down
Outlook
In general, low blood pressure will not cause additional health issues. However, it can increase the risk of falls, which is particularly dangerous for older adults.
People with low diastolic blood pressure may also have an increased risk of heart failure, so people must manage it as well as possible.
Symptoms of heart failure include:
- shortness of breath
- persistent cough
- swelling in the lower body
- tiredness
- nausea
- confusion
- palpitations
Anyone experiencing more than one of these symptoms should seek immediate medical attention.
Summary
Diastolic blood pressure measures the pressure that blood applies to artery walls between heartbeats. When diastolic blood pressure is low, the heart receives less oxygen-rich blood between beats.
Changes in diet, exercise, and lifestyle can all help increase diastolic blood pressure.
People with low diastolic blood pressure should visit their doctor regularly. This is to ensure that the doctor quickly finds any new issues that the low blood pressure is causing.
Last medically reviewed on January 6, 2023
How we reviewed this article:
SOURCES
Share this article

Medically reviewed by Megan Soliman, MD — By Anna Smith Haghighi — Updated on January 11, 2023
Latest news
- Could a vibrating, ingestible capsule help treat obesity?
- Being overly optimistic may be linked to poor decision-making
- What is a fasting-mimicking diet, and how does it benefit cardiovascular health?
- Benefits of running in the cold outweigh warm weather running
- Holiday desserts: Are Great British Bake Off recipes unhealthy?
Was this article helpful?
Understanding blood pressure readings
Blood pressure is the force of a person’s blood pushing against their artery walls. A person’s blood pressure can become too low or too high. When it becomes too high, it can lead to potential health complications.
Often, people do not experience symptoms of high blood pressure, or hypertension. This means that it is important for people to get their blood pressure checked regularly, particularly if they are older or have a history of heart complications.
High blood pressure can also lead to other complications, such as:
- eye problems
- stroke
- kidney failure
- heart disease
This article explains everything that a person needs to know about blood pressure readings and what they mean.
Systolic and diastolic

A blood pressure measurement involves two numbers that indicate the amount of pressure the blood is exerting against the arteries’ walls.
- Systolic: This is the first number. This indicates the amount of pressure that the blood exerts against the artery walls as the heart contracts.
- Diastolic: This is the second number. This shows the amount of pressure that the blood exerts against the artery walls as the heart relaxes.
Both numbers are equally significant because they provide insight into a person’s heart health. However, doctors and healthcare professionals often give systolic blood pressure more attention as they consider it a major risk factorTrusted Source for cardiovascular disease in some people.
The difference between blood pressure and pulse?
Blood pressure refers to the force of blood against the artery walls, whereas a person’s pulse indicates the number of times the heart beats per minute.
A resting heart rate is when a person is sitting, lying down, or not engaged in an activity.
An active heart rate is when a person is exercising or engaged in physical activity.
Everyone has a slightly different resting heart rate, but the average rateTrusted Source is between 60 and 100 beats per minute. A physically active person may have a heart rate as low as 40 beats per minute.
Similarly to blood pressure, a person’s heart rate or pulse indicates how healthy the heart is.

HEALTHLINE RESOURCE

Free Cholesterol-Lowering Tips — All Medically Reviewed
Get our cholesterol micro-lessons to support you in making lasting lifestyle changes to manage your cholesterol levels. Our experts have gathered cholesterol-lowering tips into free weekly 5-min lessons.
What is a normal reading?
According to the American Heart Association (AHA)Trusted Source, a normal blood pressure range is lower than 120/80 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg). When a person’s blood pressure is higher than the normal range, they may have elevated blood pressure or hypertension.
A person’s blood pressure can also drop too low. A lower than normal blood pressure can also lead to health issues.
If it drops too low, a person may feel faint, lightheaded, or dizzyTrusted Source. If a person has consistently low readings, they should talk to their doctor.
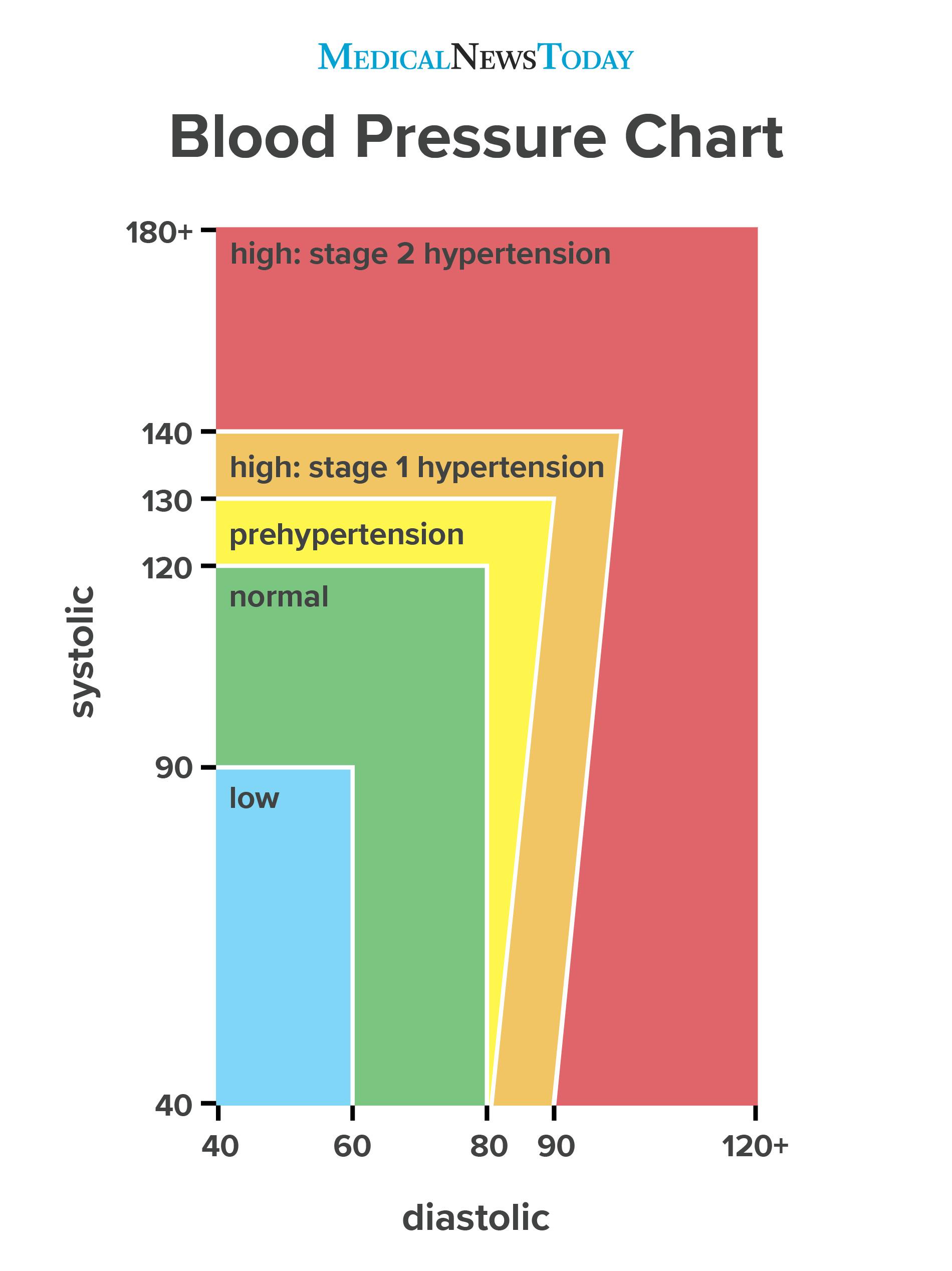
Blood pressure categories
There are five categoriesTrusted Source of blood pressure:
Normal range
According to the AHA, a normal blood pressure reading is no more than 120/80 mm Hg. Consistently higher numbers may mean a person has elevated blood pressure or hypertension.
Elevated range
An elevated blood pressure range occurs when a person has a systolic reading of between 120–129 and a diastolic reading below 80.
A person with elevated blood pressure is more likely to develop hypertension unless they take steps to lower it.
Hypertension: Stage 1
A person who has stage 1 hypertension consistently has blood pressure readings of between 130–139 systolic and 80–89 diastolic.
A doctor will likely advise a person to make lifestyle changes and may also prescribe blood pressure medication to reduce the risk of having a heart attack or stroke.
Hypertension: Stage 2
A person who has stage 2 hypertension consistently has blood pressure readings that are around 140/90 mm Hg or higher.
A person will likely need to take blood pressure medication and make lifestyle changes to help lower their blood pressure.
Hypertensive crisis
A hypertensive crisis occurs if a person suddenly has a blood pressure reading of 180/120 mm Hg. If this occurs, a person should wait for 5 minutes and remeasure their blood pressure. If the readings are still high, seek medical help from the doctor.
A person may be experiencing organ damage if the readings are high, and they develop these symptoms:
- shortness of breath
- numbness or weakness
- change in vision
- chest pain
- back pain
- difficulty speaking
If a person experiences these symptoms, they should call 911 immediately.
When to see a doctor
If someone is experiencing a hypertensive crisis, along with signs of organ failure, they should seek emergency medical help.
A person with a history of heart disease, heart attack, stroke, or other cardiac issues should regularly see their doctor for blood pressure checks. They may also want to check their pressure at home regularly.
A person should see their doctor if their blood pressure is higher than the normal readings to understand what the cause is and how to treat it.
Summary
People measure blood pressure using two numbers that represent the pressure the blood exerts on the arteries as the heart contracts and relaxes.
Doctors consider a person’s blood pressure to be in the normal range when they have readings consistently below 120/80.
Higher readings can indicate a person has elevated or hypertension. If left untreated, this can lead to cardiac issues.
A person can make changes in their diet and exercise regime to help keep their blood pressure under control.
Last medically reviewed on December 3, 2019
How we reviewed this article:
SOURCES
Share this article

Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI — By Jenna Fletcher on December 3, 2019
Latest news
- Could a vibrating, ingestible capsule help treat obesity?
- Being overly optimistic may be linked to poor decision-making
- What is a fasting-mimicking diet, and how does it benefit cardiovascular health?
- Benefits of running in the cold outweigh warm weather running
- Holiday desserts: Are Great British Bake Off recipes unhealthy?
Was this article helpful?
High cholesterol, high blood pressure before age 55 increases the risk of heart disease in later years
- Researchers are reporting that hypertension and high cholesterol before age 55 can increase the risk of heart disease later in life.
- They note that this risk remains, even if the individual takes steps to control these conditions after age 55.
- The researchers said that heart disease is typically a result of a cumulation of risk factors, including genetics. However, as people age, genetics play less of a role.
Having high blood pressure and/or high cholesterol before age 55 can increase the risk of heart disease, even in people who improve those conditions as they get older.
Those findings are part a studyTrusted Source published today in the journal PLOS ONE.
The researchers used a 3-sample randomization analysis of participants who were registered with the UK Biobank.
There were three groups in the analysis:
- 136,648 people had high cholesterol (LDL-C)
- 135,431 people had elevated systolic blood pressure (SBP)
- 24,052 people had coronary heart disease
What researchers learned from heart disease study
The researchers noted that when high LDL-C and SBP could be predicted based on genetics, there was a risk of coronary heart disease, regardless of the age of diagnosis.
They also pointed out that those with elevated SBP and LDL-C in early to midlife were at an increased risk of coronary heart disease, independent of their SBP and LDL-C levels in later life.
The researchers also noted that coronary heart disease is generally a result of cumulative exposure to risk factors, such as SBD and LDL-C, and these can have long-lasting implications on a person’s risk.
They added that the effects of SBP on coronary heart disease diminished with age, nothing that this could be due to a previous observationTrusted Source that the effects of genetic on several diseases begin waning later in life.
In their discussions of study results, the researchers also point out that their findings are consistent with randomized controlled trials that suggest the use of blood pressure medications and statins can help, even in old age. Despite this, they say the use of statins and blood pressure medicine often declines with age.
The researchers suggest that treating young individuals with elevated SBP and/or LDL-C is essential to minimize accumulated exposure throughout their lives.
“Our findings suggest that old age alone should not be a reason to withhold otherwise appropriate LDL-C and BP-lowering treatments, because the effect of genetically mediated LDL-C and SBP on the incident risk of [coronary heart disease] is consistent throughout life,” they wrote.
Experts weigh in on cholesterol, hypertension study
“We have known that high blood pressure and elevated cholesterol are risk factors for heart disease,” said Dr. Cheng-Han Chen, an interventional cardiologist and medical director of the Structural Heart Program at MemorialCare Saddleback Medical Center in California who was not involved in the research. “This study examines the relationship over a long time and adds to our understanding of the relationship in different age groups.”
“It will not change how I treat my patients as I already treat hypertension and high cholesterol throughout a person’s lifespan,” Chen told Medical News Today. “I already treat people under 55 for both high cholesterol and high blood pressure.”
Dr. Yu-Ming Ni, a cardiologist and lipidologist at MemorialCare Heart and Vascular Institute at Orange Coast Medical Center in California who was not involved in the study, agrees that the research isn’t going to change his overall scope of treatment.
However, Ni said he might be more aggressive in managing cholesterol at a younger age.
“I might talk to my younger patients who have more chances of making changes to diet/lifestyle, better explain the risks, and work with them on changes they can make in their daily lives,” he told Medical News Today.
“As we age, other factors take over, such as smoking, sedentary lifestyle, and poor eating habits, and take over the role of genetics,” Ni added. “When that happens, we need to modify these things to lower our risk of high cholesterol. This study shows that the longer you have high cholesterol, the higher your chance of heart disease.”
“I like the studies using the UK Biobank because they have a large pool of people to draw from,” Ni said. “The results are reliable.”
The researchers noted that their study did have limitations. For example, the use of antihypertensives and lipid-lowering medications varied between age groups. To help account for this, the researchers adjusted SBP and LDL-C based on treatment status.

HEALTHLINE RESOURCE

Free Cholesterol-Lowering Tips — All Medically Reviewed
Get our cholesterol micro-lessons to support you in making lasting lifestyle changes to manage your cholesterol levels. Our experts have gathered cholesterol-lowering tips into free weekly 5-min lessons.
Risk factors for high blood pressure, cholesterol
Experts say that lifestyle factors play a significant role in both high cholesterol and blood pressure.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and PreventionTrusted Source (CDC), some of the risk factors for high blood pressure include:
- Unhealthy diet, especially those that are high in sodium and low in potassium
- Physical inactivity
- Obesity
- Misuse of alcohol
- Smoking or other tobacco use
The CDCTrusted Source lists risk factors for high cholesterol as:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Obesity
- Diets high in saturated and trans fats
- Physical inactivity
- Smoking
Poor diet, obesity, physical inactivity, and smoking are on both lists.
Share this article

By Eileen Bailey on December 20, 2023 — Fact checked by Jill Seladi-Schulman, Ph.D.
Latest news
- Could a vibrating, ingestible capsule help treat obesity?
- Being overly optimistic may be linked to poor decision-making
- What is a fasting-mimicking diet, and how does it benefit cardiovascular health?
- Benefits of running in the cold outweigh warm weather running
- Holiday desserts: Are Great British Bake Off recipes unhealthy?
Was this article helpful?
Get our newsletter
Keep up with the ever-changing world of medical science with new and emerging developments in health.SUBSCRIBE










